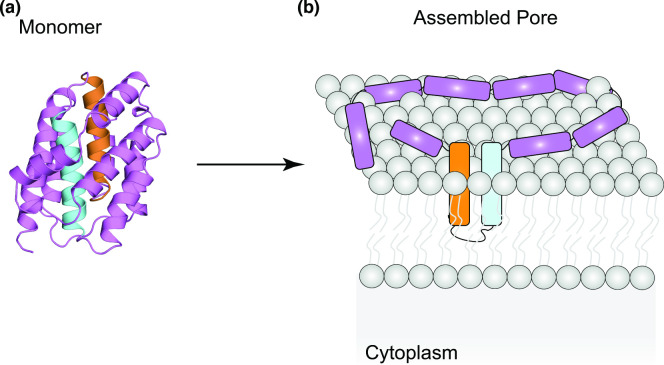
Fig. 5.
(a) Structure of the soluble monomer of colicin A (PDBID: 1COL). The pair of hydrophobic helices are depicted in cyan and orange. (b) Schematic depiction of the ‘umbrella model’ of colicin pore-formation, adapted from Cascales et al. (2007) [158]. Here, the pair of hydrophobic helices (in cyan and orange) are inserted in the membrane to constitute the pore, while the remaining helices lie on the membrane surface. Colicin oligomerisation and/or involvement of lipids as structural elements are then employed to form the final, active pore.