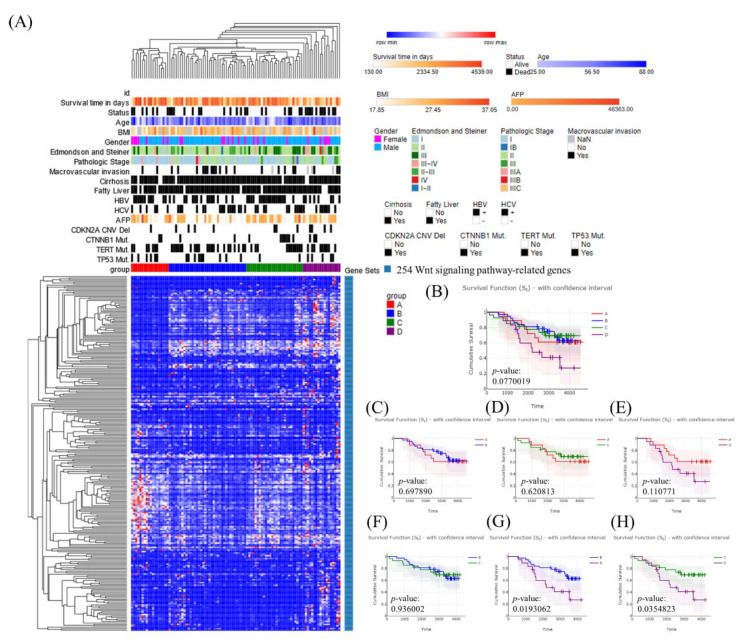
Figure 1.
Molecular classification of Taiwanese hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) using a panel of 254 Wnt pathway genes. (A) Heatmap showing normalized expression levels of 254 signature genes (rows) across subjects (columns) divided into four molecular subclasses (A–D) using an unsupervised approach. Each signature gene was significantly up- or downregulated in one subclass relative to the other subclasses, as indicated by color changes, where blue and red indicate low and high expression, respectively. Signature genes and subjects were hierarchically clustered within each subclass. Significant differences in demographic characteristics, clinical annotations, molecular subclasses, and hepatitis B and C virus infection status across subjects are shown at the top of the figure. (B–H) Overall survival of subjects in each molecular subclass.