Figure 5.
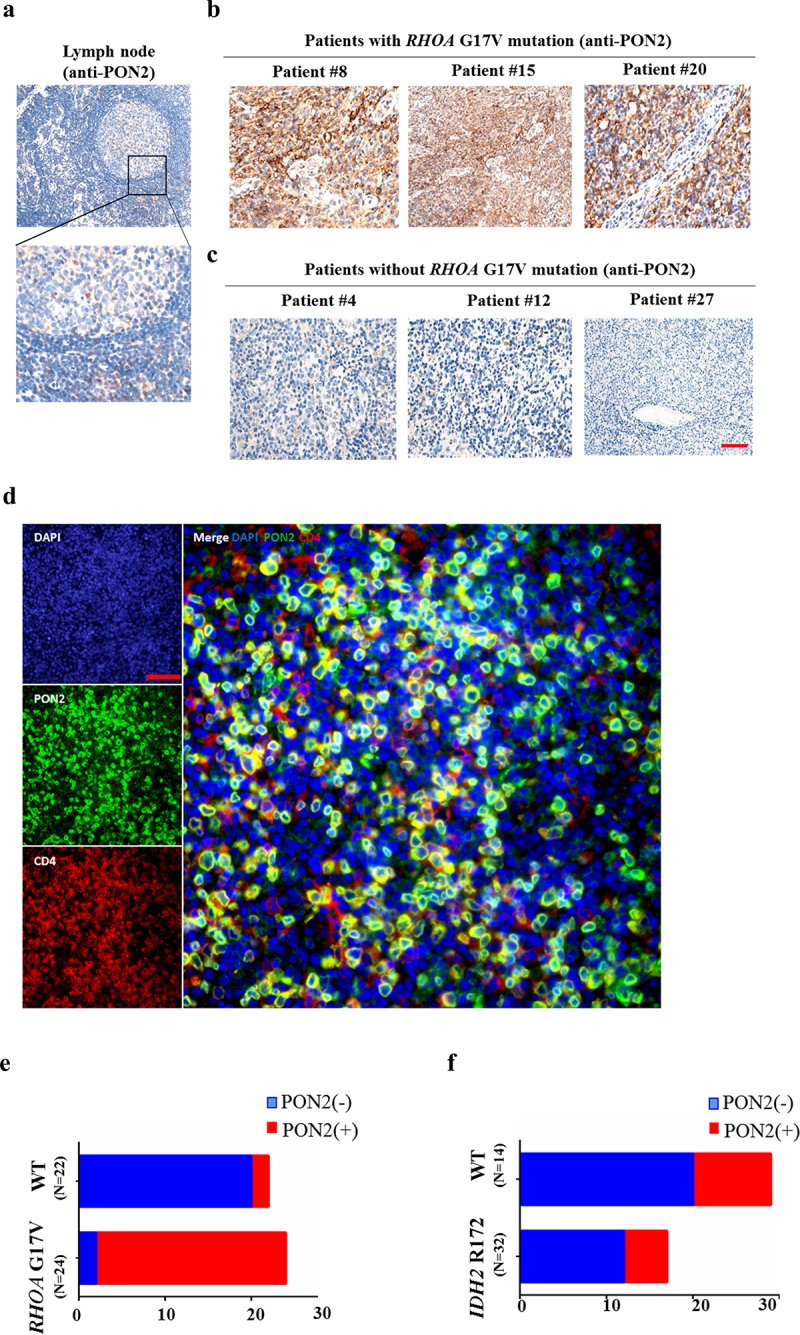
PON2 expression is associated with RHOA G17V mutation in AITLs. (a–c) Immunohistochemical analysis of PON2 distribution in normal human lymph nodes (a) and lymphoma biopsies isolated from patients with AITLs bearing RHOA G17V mutation (b) or without RHOA G17V mutation (c). EliVision Plus two-step immunohistochemical technique with 3–3’ diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining was used. Original magnification: × 400. scale bar: 10 µm. (d) Detection of PON2 in AITL cells by Multiplexed fluorescence immunohistochemistry. Left upper panel shows conventional DAPI staining. Left middle panel shows the single PON2 staining in green. Left lower panel shows the single CD4 staining in red. Right panel shows the multiplexed fluorescence staining of PON2 and CD4. Original magnification: × 200; scale bar: 100 µm. (e) The histogram illustrates the percentage of PON2 immunostaining in AITLs bearing RHOA G17V mutation or without RHOA G17V mutation. AITLs with RHOA G17V mutation showed significantly higher PON2 expression levels than AITLs with RHOA wild-type (WT) (chi-square test, P = .002). (f) The histogram illustrates the percentage of PON2 immunostaining in AITLs bearing IDH2 R172 mutation or without IDH2 R172 mutation. There was no difference in PON2 immunostaining between AITLs with IDH2 R172 mutation or without IDH2 R172 mutation (chi-square test, P = .908).
