Figure 1. Decoding MAMPs and DAMPs by the cognate receptors.
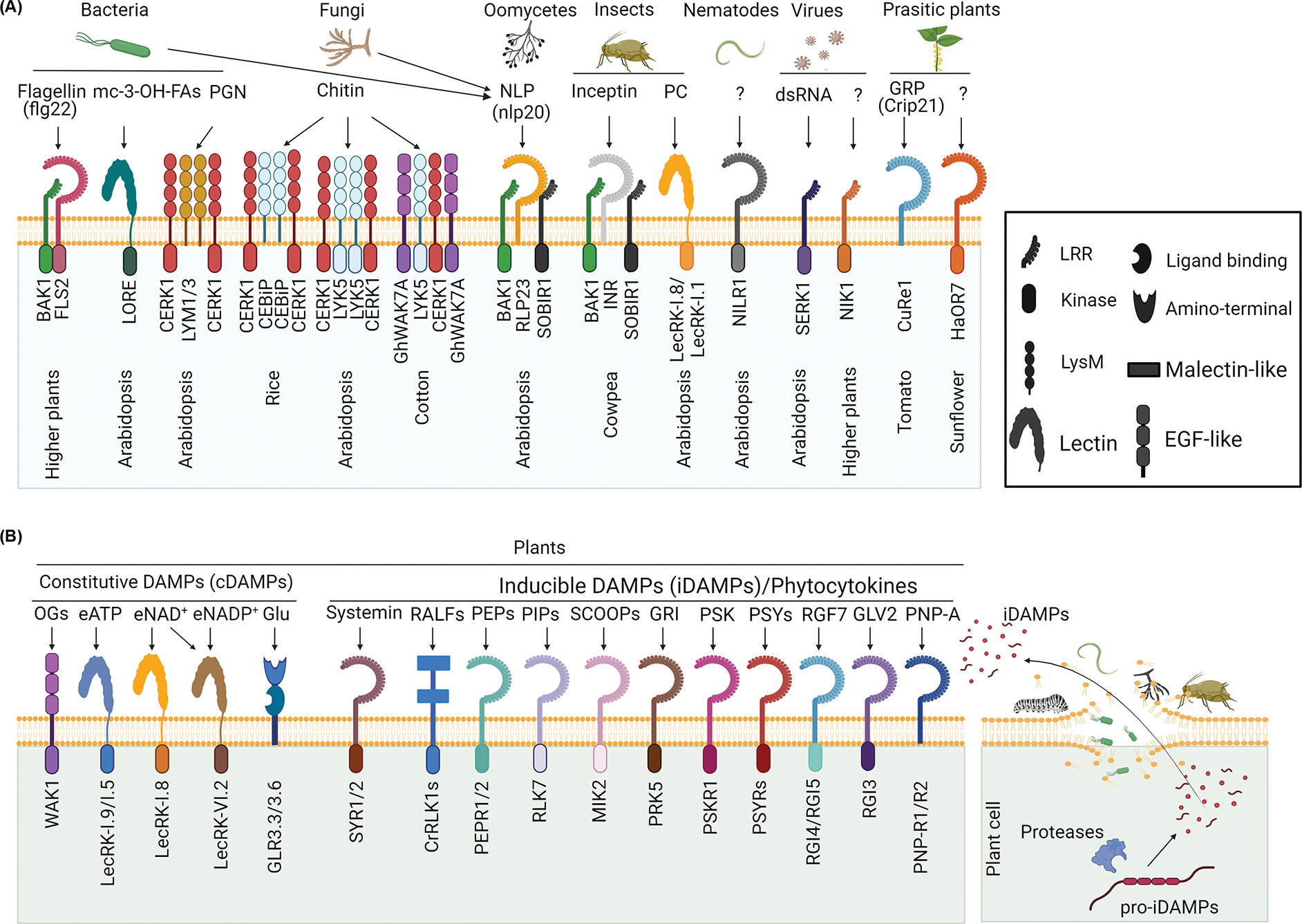
(A) Recognition of diverse MAMPs from bacteria, fungi, oomycetes, insects, nematodes, viruses, and parasitic plants by plant PM-resident PRRs. The bacterial flagellin or flg22 peptide is perceived by the LRR-RLKs FLS2 in complex with BAK1. Free mc-3-OH-FAs are recognized by LecRK LORE. Bacterial PGN is sensed by LysM-RLPs LYM1 and LYM3 with LysM-RLK CERK1. Fungal chitin is perceived by LysM-RLP OsCEBiP and OsCERK1 in rice, LysM-RLK LYK5 and CERK1 in Arabidopsis, and LysM-RLKs GhGLYK5 and GhCERK1 in cotton. Bacterial, fungal, and oomycete necrosis and ethylene-inducing peptide 1 (Nep1)-like protein (NLP) is recognized by RLP23 in complex with SOBIR1 and BAK1. Inceptin from herbivore oral secretions is recognized by LRR-RLP inceptin receptor (INR) in complex with SOBIR1 and SERKs. Insect egg-derived phosphatidylcholine (PC) is identified as an EAMP signaling through lectin receptor kinase-I.1 (LecRK-I.1) and LecRK-I.8. Nematode-induced LRR-RLK 1 (NILR1) is required for basal resistance to nematodes. Viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) stimulates PTI responses requiring SERK1, and LRR-RLK NIK1 positively regulates plant antiviral immunity. The parasitic plant Cuscuta reflexa cell wall protein CrGRP is sensed by tomato LRR-RLP CuRe1 by recognizing the epitope, Crip21. LRR-RLK HaOR7 from sunflower recognizes an unknown MAMP and confers resistance against parasitic plant Orobanche cumana. (B) Recognition of DAMPs by PRRs. cDAMPs are ubiquitous molecules with essential roles in plant homeostasis and released into the apoplasts upon infections. They include oligogalacturonide (OG), eATP, eNAD(P)+, and glutamate recognized by WAK1, LecRK-I.9, and LecRK-I.5, LecRK-I.8 and LecRK VI.2, and GLR3.3 and GLR3.6, respectively. iDAMPs, termed phytocytokines, are small secretory peptides processed from precursor proteins (pro-iDAMPs) by proteases upon infections and cell damages (right). Several well-studied iDAMPs and their receptors are shown on the left. Abbreviations: CERK1, chitin elicitor receptor kinase 1; CuRe1, Cuscuta receptor 1; eATP, extracellular adenosine 5′-triphosphate; eNAD(P)+, extracellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides in their phosphorylated or unphosphorylated forms; GLR, glutamate receptor-like; NIK1, NSP-interacting kinase 1; SOBIR1, suppressor of BIR1.
