Figure 2. Mutual potentiation and/or attenuation of immunity by MAMPs and DAMPs and pathogen mimicry.
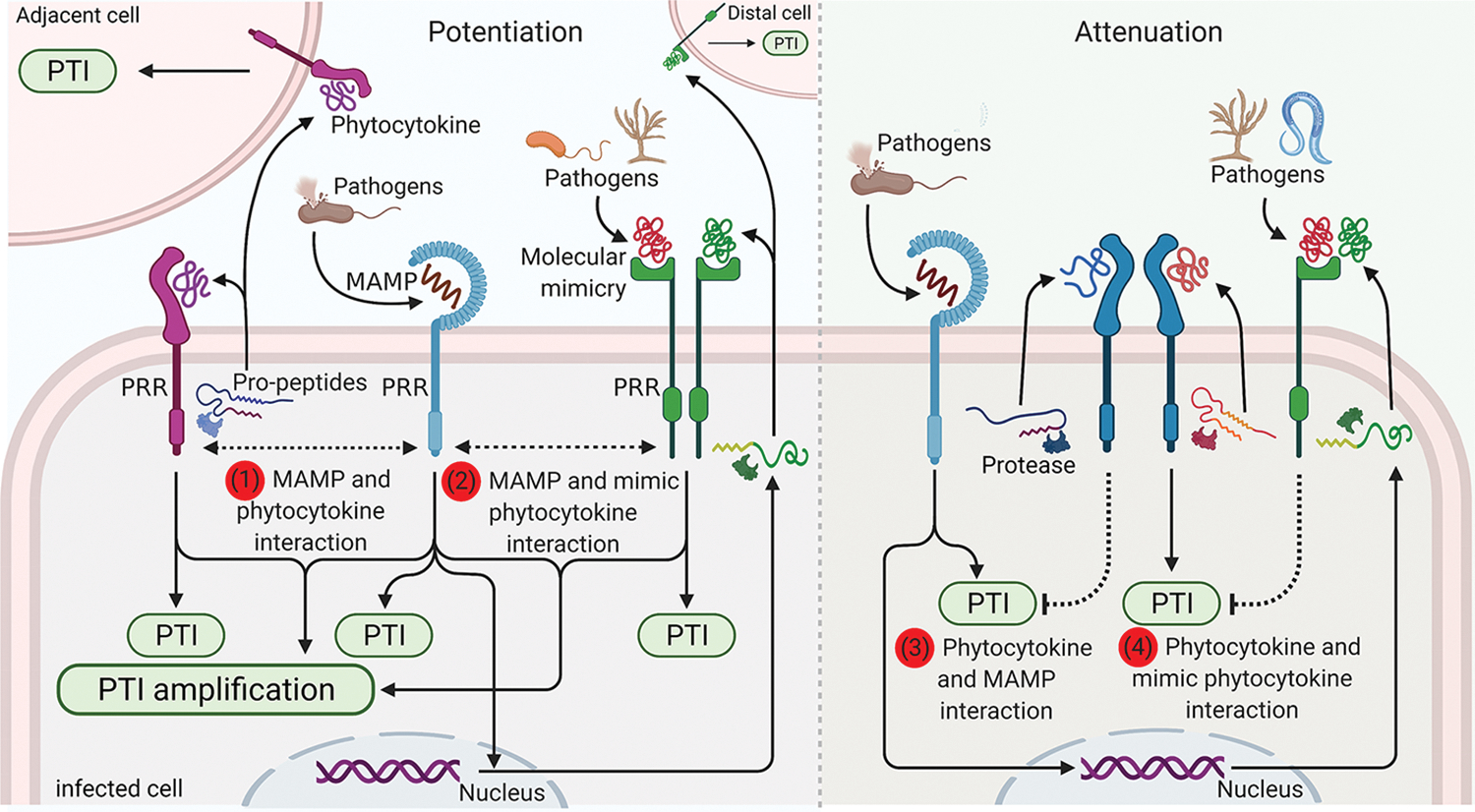
Perception of MAMPs, phytocytokines, and pathogen-derived phytocytokine-mimic peptides by PRRs induces the PTI signaling via acting on the same infected cell, adjacent cells, or distal cells. Pathogen infections or MAMP perceptions induce the production of DAMPs and phytocytokines, which further modulate the PTI signaling. Phytocytokines (1) and pathogen mimicries (2) mutually amplify MAMP-induced defense responses. Moreover, host-derived phytocytokine (3) or pathogen-derived phytocytokine-mimic peptides (4) can interfere with and attenuate the MAMP-or host phytocytokine-mediated immune signaling. All figures were generated using BioRender (biorender.com).
