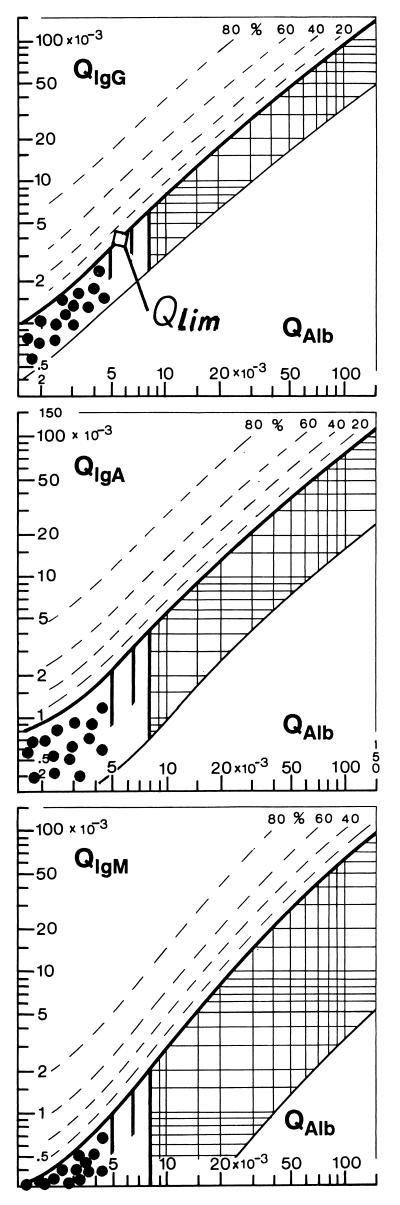
FIG. 1.
CSF/serum quotient diagrams for IgG, IgA, and IgM (Reiber graphs). The reference range of blood-derived IgG, IgA, and IgM concentrations in CSF include 99% (±3 s) of the group investigated (9). The upper hyperbolic curves (thick lines) represent the discrimination lines between brain-derived and blood-derived immunoglobulin fractions. Values above these upper discrimina- tion lines represent intrathecal IgG, IgA, or IgM synthesis. The dashed lines indicate the extent of intrathecal synthesis as intrathecal fractions (IgGIF, IgAIF, or IgMIF) with 20, 40, 60, and 80% of the measured total immunoglobulin concentration in CSF, with reference to the discrimination line as 0% intrathecal synthesis. The limit of the reference range for QAlb between normal and increased CSF protein concentrations due to blood-CSF barrier dysfunction is indicated by the age-dependent vertical lines at QAlb = 5 · 10−3 (up to 15 years), at QAlb = 6.5 · 10−3 (up to 40 years), and at QAlb = 8 · 10−3 (up to 60 years). The diagrams depict the following ranges: 1, normal; 2, blood-CSF barrier dysfunction (i.e., reduced CSF turnover); 4, intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis with no change in CSF turnover; 3, intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis with reduced CSF turnover. Values below the lower hyperbolic line in range 5 indicate a methodological fault. The data of 15 control patients (•) are representative of the age-related normal range with normal blood-CSF barrier function and no intrathecal immunoglobulin synthesis.