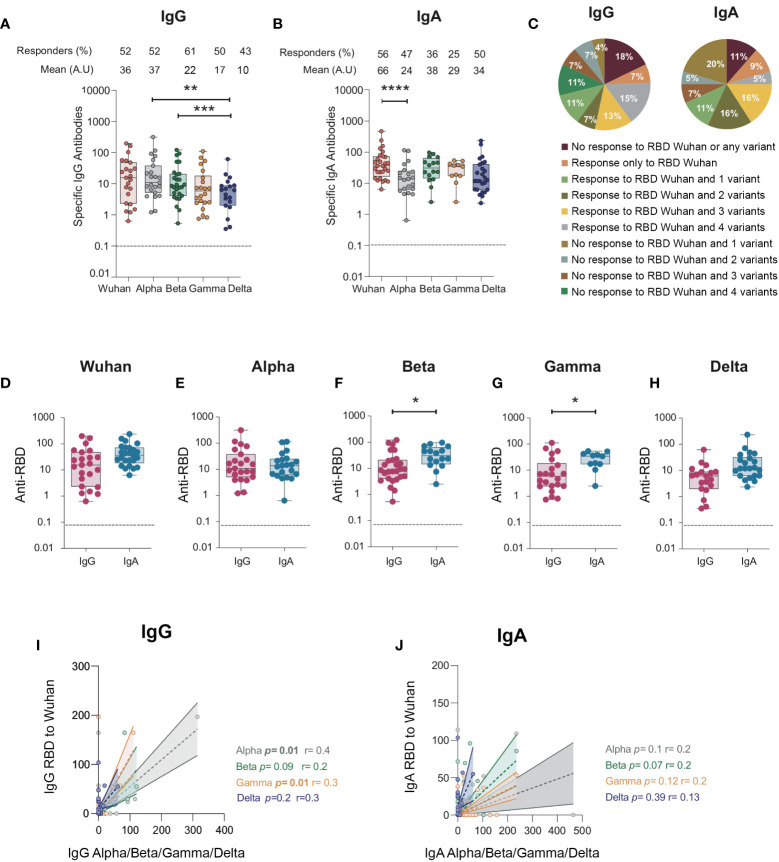
Figure 4.
IgG and IgA antibodies from BAL from SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals against RBD protein from SARS-CoV-2 Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), Gamma (P.1), and Delta (B.1.617) variants. (A) Specific IgG responses against Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta RBD in BAL from SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals. (B) Specific IgA responses against Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta RBD in BAL from SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals. (A, B) Proportion of specific IgG or IgA over total IgG or IgA measured by ELISA (specific (OD450)/total IgA or G (μg/ml)) are shown. (C) Pie charts showing the percentages of the different responses of IgG (left) and IgA (right) to Wuhan RBD and the different variants. (D–H) Comparison between specific IgG and IgA responses detected against the RBD from ancestral Wuhan strain (D), Alpha (E), Beta (F), and Gamma (G)and Delta (H) variants. Correlation between IgG (I) and IgA (J) specific to Wuhan RBD and IgG and IgA antibodies specific for Alpha, Beta and Gamma variants. Correlations were calculated using Spearman’s test. p-Values were calculated by using Wilcoxon test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.005, ****, p < 0.0001. Dashed line: cutoff value for antibody detection. BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; RBD, receptor-binding domain.