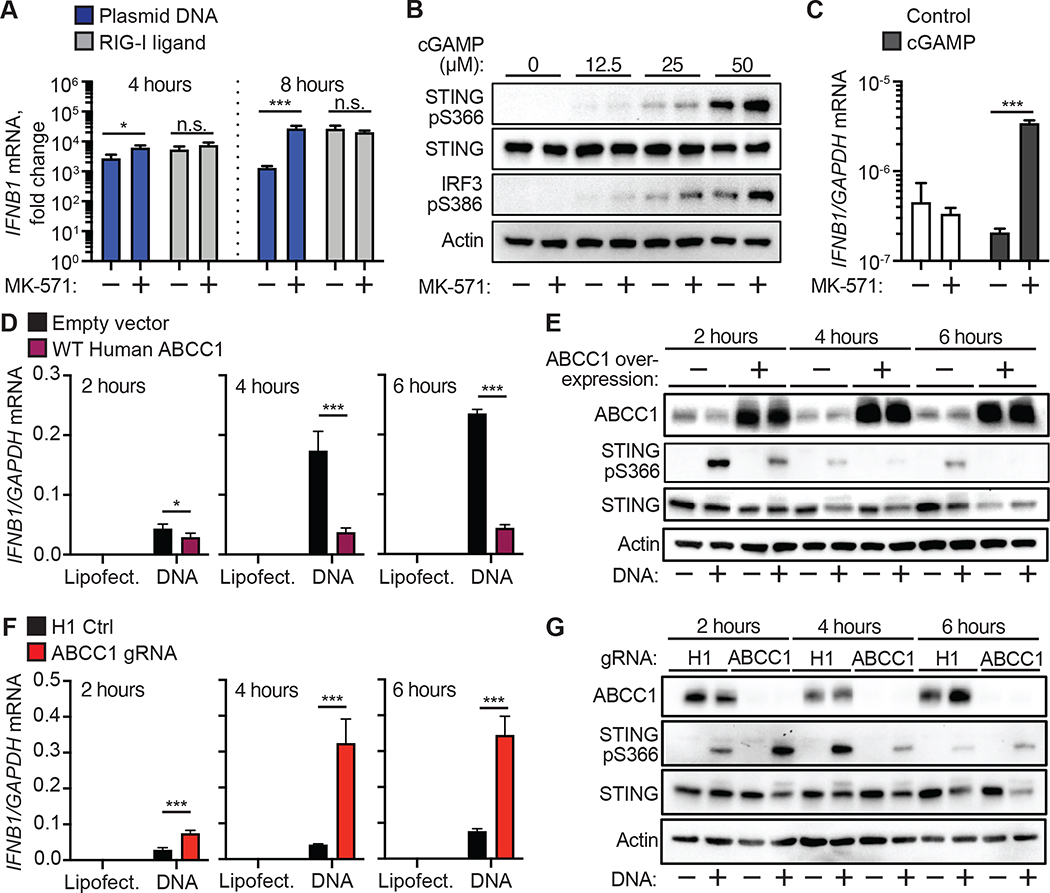
Figure 6. cGAMP export controls cell-intrinsic STING signaling.
(A) Quantification of IFNB1 induction by RT-qPCR in HFFs that were treated with 25 μM MK571 or mock followed by transfection with plasmid DNA or RIG-I ligand for 4 or 8 hrs.
(B) HFFs were treated with 25 μM MK-571 or mock, and then cGAMP (0–50 μM) was added to the extracellular media. Immuno blot analysis was performed 4 hours after cGAMP addition for phosphorylated STING, STING, and phosphorylated IRF3.
(C) HFFs were treated with 25 μM MK-571 or mock, and then cGAMP (0 or 50 μM) was added to the extracellular media. INFB1 induction was quantified by RT-qPCR 4 hours after cGAMP addition.
(D) Quantification of IFNB1 induction by RT-qPCR in HFFs overexpressing ABCC1 or empty vector control following transfection with CT DNA. Cells were harvested at the indicated time points.
(E) Immuno blot analysis of cells from (D) for ABCC1, phosphorylated STING, and STING protein expression.
(F) Quantification of IFNB1 induction by RT-qPCR in ABCC1- or H1 control-targeted HFFs following transfection with CT DNA. Cells were harvested at the indicated time points.
(G) Immuno blot analysis of cells from (F) for ABCC1, phosphorylated STING, and STING protein expression. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-way ANOVA comparing mock or MK-571 treatment within each transfected ligand group (A, C) or comparing control to ABCC1-modulated cells within each transfected ligand group (D, F). All tests were corrected for multiple comparisons using the Holm-Sidak method. Error bars represent mean ± SD of three biological replicates per group. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001. All data shown are derived from a single representative experiment. Comparative results were obtained across three independent experiments.