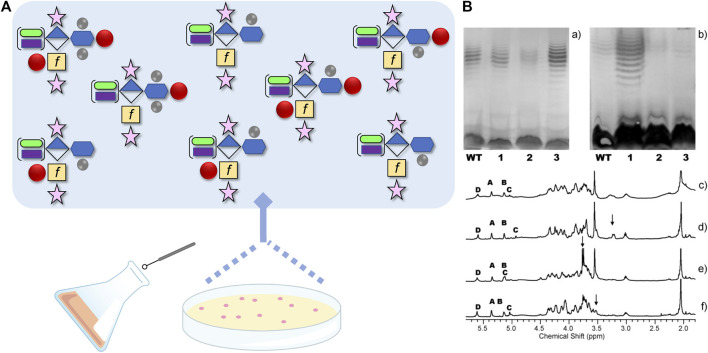
FIGURE 3.
(A) Schematic demonstrating the reported capsular polysaccharide (CPS) structures originating from Campylobacter jejuni strain NCTC 11168, from ~ 1000 possible structures, using the Symbol Nomenclature for Glycans with some modifications. The CPS structure shown is the [→ 2)-β-D-Ribf-(1–5)-β-D-GalfNAc-(1–4)-α-D-GlcA6(NSel)-(1 →]n repeating unit with D-glycero-α-L-gluco-Hep (blue hexagon) at C-3 of GlcA (diamond). The Hep can be further modified+/-3O-Me, 6O-Me (methyl groups are grey circles) and/or O-4 MeOPN (methyl phosphoramidate drawn as red circle). In addition, the GalfNAc (yellow square with f to designate furanose form) can be modified at O-3+/-MeOPN, and GlcA6 can be modified with either NSel (N-serinol, green oval) or NEtN (N-ethanolamine, purple rectangle). Ribose is shown as the pink star. (B) Original image from Szymanski et al., 2003 showing differences in CPS structures (c-f), and their corresponding silver-staining (a) and immunoreactivity (b) from single colony isolates originating from same culture. (a) Silver-stained deoxycholate-PAGE and (b) western blot detected with HS:2 typing sera both showing: lane 1, NCTC 11168 wildtype population; lane 2, 11168 variant one; lane 3, 11168 variant two; and lane 4, 11168 variant 3. (c-f) High resolution magic angle spinning (HR-MAS) NMR spectra of the wildtype population (c), variant 1 with arrow indicating ethanolamine resonance (d), variant 2 with arrow indicating MeOPN modification identified for the first time (e), and variant 3 with the arrow indicating loss of OMe resonance (f). Anomeric resonances in c-f are labeled A (Ribf), B (GlcA6), C (GalfNAc), and D (Hep). See (Szymanski et al., 2003) for more information.