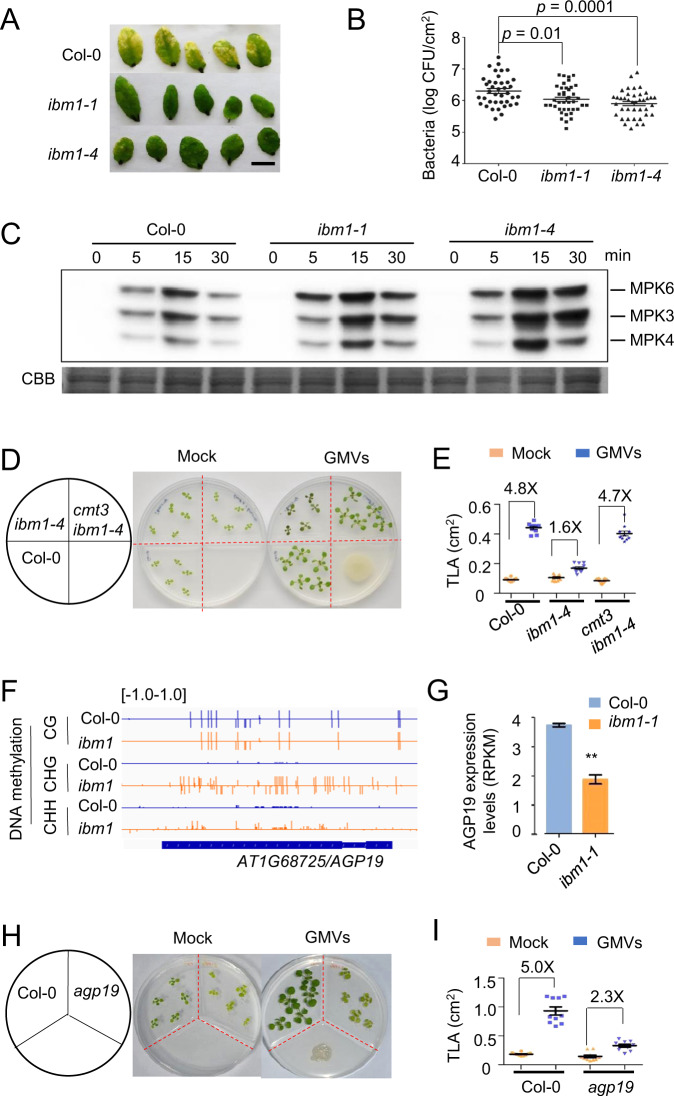
Fig. 4. IBM1 dysfunction increases plant disease resistance and impairs growth promotion triggered by beneficial bacteria.
A The disease resistance phenotype of ibm1-1, ibm1-4, and Col-0. Five-week-old plants were injection-inoculated with Pst. DC3000 (105 cfu/mL). The leaves shown were photographed at 5 dpi (days post inoculation). Scale bar = 1 cm. B Bacterial growth of Pst. DC3000 on plants at 3 dpi. Mean ± SE, n = 40 individual plants. Student’s t-test p values are shown. C Flg22-induced MPK3/MPK6 phosphorylation is enhanced by IBM1 dysfunction. Kinase assays were performed with samples harvested at 0, 5, 15, and 30 min after the flg22 treatments. Two independent experiments were performed with similar results. D IBM1 dysfunction impairs plant growth promotion triggered by GB03-produced microbial volatiles (GMVs); the impairment can be rescued by a second mutation of cmt3 in the ibm1 mutant. Images were taken at 7 days after treatment (DAT). Red-dotted lines indicate inner plastic partitions that divide the plate into four parts. E Quantification of total leaf area per seedling (TLA) of the plants at 7 DAT. Mean ± SE, n = 15. All fold changes are associated with statistical significance of p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). F IBM1 dysfunction increases DNA methylation levels in the CHG and CHH contexts at the AGP19 locus. A snapshot from whole-genome bisulfite sequencing is shown. G IBM1 dysfunction decreases the mRNA level of AGP19. Bars show the FPKM values from the RNA-seq results. Mean ± SE, n = 3 biological replicates. Double asterisks indicate statistical difference with p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). H The agp19 null mutant showed impaired plant growth promotion by GMVs. Images were taken at 7 days after treatment (DAT). I Quantification of total leaf area per seedling (TLA) of the plants at 7 DAT. Mean ± SE, n = 15. All fold changes are associated with statistical significance of p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test).