FIGURE 8:
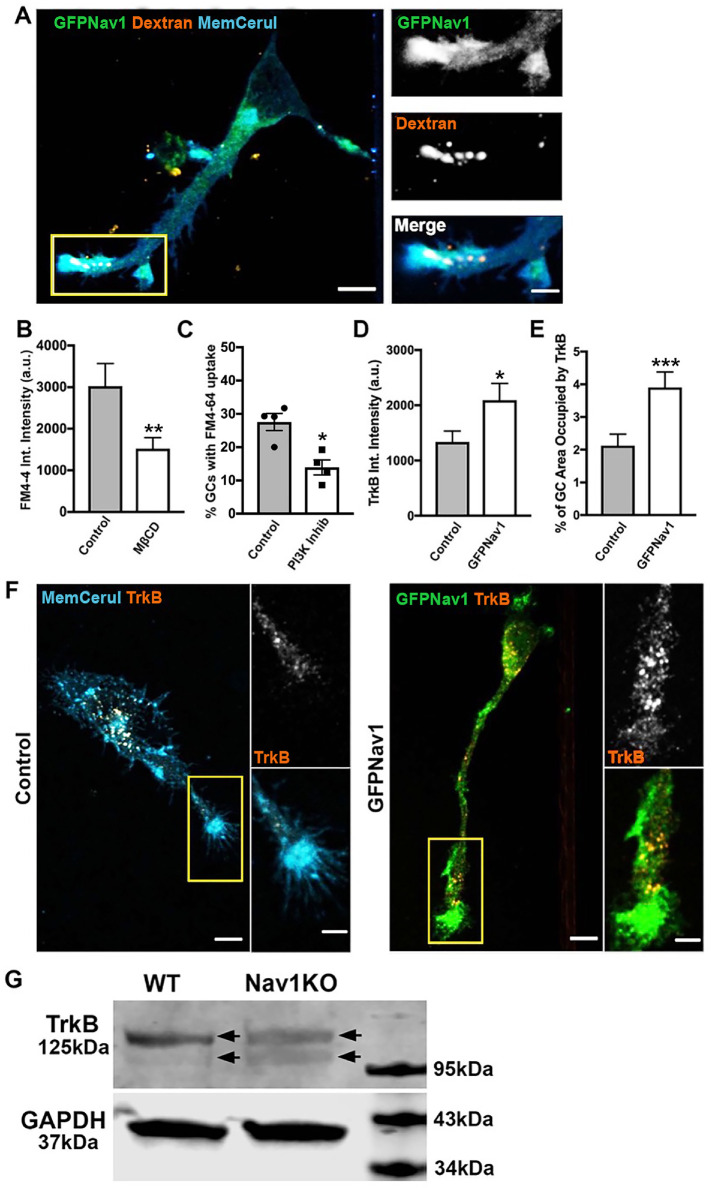
Nav1 promotes macropinocytosis and growth factor internalization at the growth cone. (A) Representative image of 3 DIV hippocampal neurons transfected with GFP-Nav1 (green) and pcs-CeruleanMembrane-FP (blue) and incubated with 70 kDa dextran (red) showing that high-molecular-weight dextran is taken up in Nav1-enriched growth cones. Scale bar = 10 μm, 5 μm for zoomed images. (B) MβCD treatment of GFP-Nav1–transfected primary neurons decreases FM4-64 uptake in growth cones. Statistical analysis: Mann–Whitney, **p < 0.01; n = 3 experiments; control = 46 growth cones, MβCD = 53 growth cones. (C) PI3 kinase inhibition of GFP-Nav1–transfected primary neurons decreases the number of growth cones with FM4-64 uptake. Statistical analysis: Mann–Whitney, *p < 0.05; n = 4 experiments; DMSO = 199 growth cones, PI3K Inhib = 179 growth cones. (D) Growth cones of primary neurons expressing GFP-Nav1 have significantly more TrkB internalization by intensity than control growth cones. Statistical analysis: Mann–Whitney, *p < 0.05; n = 3 experiments; control = 61 growth cones, GFP-Nav1 = 60 growth cones. (E) Growth cones of primary neurons expressing GFP-Nav1 have significantly more TrkB internalization by percent area occupied than control growth cones. Statistical analysis: Mann–Whitney, ***p < 0.001; n same as in D. (F) Representative images of control and GFP-Nav1 primary neurons, expressing pcs-CeruleanMembrane-FP or GFP-Nav1 and pcs-CeruleanMembrane-FP, respectively, after internalization of the TrkB 1D7 antibody. Scale bar = 10 μm, 5 μm for zoomed images. (G) Representative Western blot of 4 d retinoic acid–differentiated WT and Nav1KO SH-SY5Y cells showing a double band (arrows indicate each band of doublet) for TrkB. GAPDH included as a loading control. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Images represent observations from three individual culture preparations.