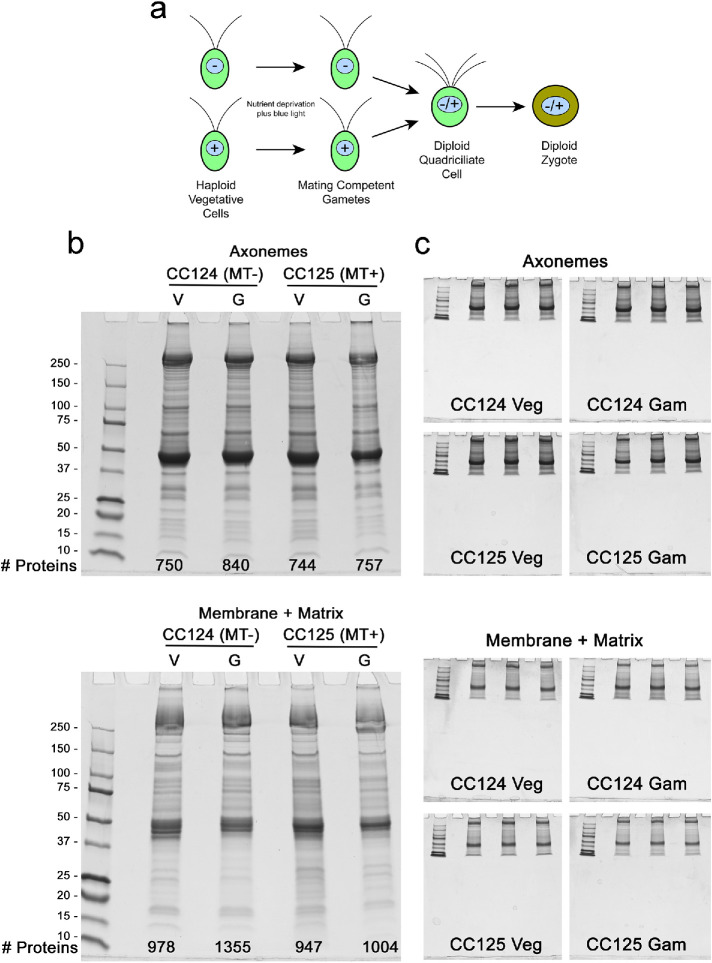
FIGURE 1:
Cilia samples used for mass spectrometry. a) Schematic illustrating the transition from vegetative to gametic Chlamydomonas cells, and formation of a diploid quadriciliate cell that subsequently develops into a zygote. Mating type is indicated by – and + signs within the nucleus. b) Axoneme and detergent-soluble membrane plus matrix samples from vegetative (Veg) and gametic (Gam) cilia of wild-type Chlamydomonas of both mating types (CC124 and CC125) were electrophoresed in 4–15% gradient gels and stained with Coomassie blue; in combination, the amounts loaded for membrane plus matrix and axoneme fractions of each sample were 50 μg cilia. The number of proteins identified in each sample is indicated at the bottom of each gel. c) Additional aliquots of the samples shown in panel b were run in triplicate using a short gel format and stained with Coomassie blue. Following imaging, the protein-containing gel segments were excised, trypsinized, and subjected to mass spectral analysis.