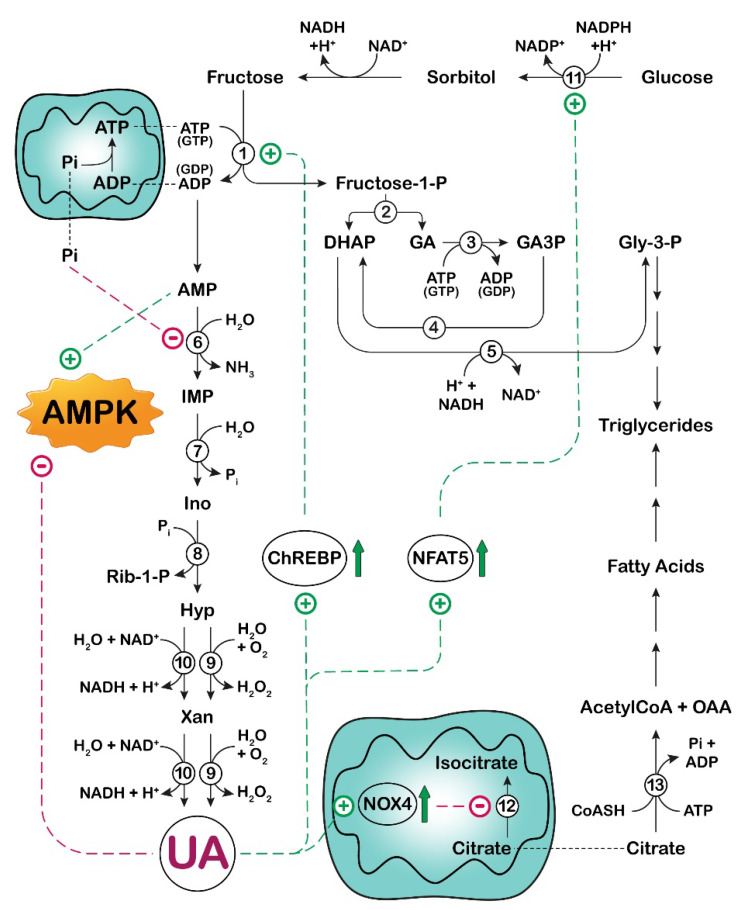
Figure 2.
Effect of UA on fructose metabolism in liver. Phosphorylation of fructose in liver is catalyzed by fructokinase (enzyme 1), which is not subjected to feedback inhibition and phosphorylates fructose as rapidly as it can, leading to intracellular ATP and phosphate depletion. The formed fructose-1-phospahte is cleaved by aldolase B (enzyme 2) into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and glyceraldehyde (GA). GA is phosphorylated to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GA3P) (triokinase, enzyme 3), which can enter the glycolytic pathway or can be converted by triose phosphate isomerase (enzyme 4) into DHAP. In turn, DHAP, by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (enzyme 5), is reduced to glycerol-3-phosphate (Gly-3-P), which contributes to the synthesis of triglycerides. As a consequence of ATP catabolism, AMP is generated. The deamination of AMP, catalyzed by AMP deaminase (enzyme 6), is accelerated, and AMP is channeled towards IMP, which is hydrolyzed by cytosolic-5’-nucleotidase II (enzyme 7) to inosine (Ino). In turn, Ino is phosphorolytically cleaved into hypoxanthine (Hyp) and ribose-1-phosphate (Rib-1-P) by purine nucleoside phosphorylase (enzyme 8). Rib-1-P can be mutated to ribose-5-phosphate and then converted to 5-phosphoribosyl-1- pyrophosphate (see Figure 3), thus contributing to the increase in purine de novo synthesis. Hyp, through the action of xanthine oxidoreductase (oxidase, enzyme 9 or dehydrogenase, enzyme 10), is converted to UA. UA exerts an inhibitory effect on AMPK (see Figure 4) and an activatory effect (through stimulation of ChREBP) on fructokinase (enzyme 1). UA also activates aldose reductase (enzyme 11) (through stimulation of NFAT5), enabling endogenous fructose production from glucose. In addition, UA promotes the translocation of NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) from cytosol to mitochondria, which increases mitochondrial ROS generation with inactivation of aconitase (enzyme 12). Citrate is released by the mitochondrion and then converted back, by cytosolic ATP-citrate lyase (enzyme 13), to acetyl-CoA, necessary for the synthesis of fatty acids and triglycerides. ChREBP: carbohydrate response element binding protein; NFAT5: nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5; OAA: oxalacetic acid; Xan: xanthine; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase;  : activation;
: activation;  : inhibition;
: inhibition;  : increase.
: increase.