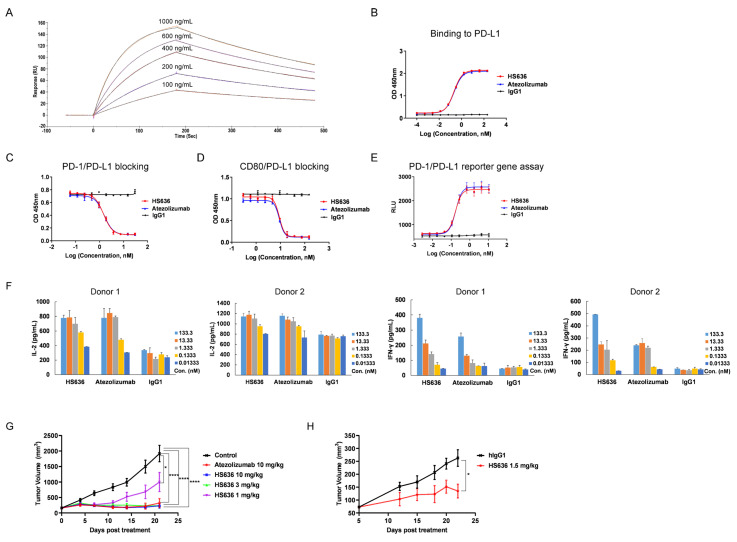
Figure 1.
In vitro functional activity and in vivo antitumor efficacy of HS636. (A)The affinity of HS636 to PD-L1 was detected by Surface plasmon resonance (SPR). (B) The binding activity of HS636 to human PD-L1 was determined by ELISA. The blocking activity of HS636 towards PD-1/PD-L1 interaction (C) and CD80/ PD-L1 interaction (D) was determined by competition ELISA. (E) The bioactivity of HS636 on PD-1/PD-L1 signaling was performed by the PD-1/PD-L1 NFAT reporter gene assay. (F) The T cell activation effect of HS636 was determined in MLR assay. CD4 + T cells from 2 donors and allogeneic DCs were co-cultured in the presence of indicated concentrations of HS636 for 3 days, then IL-2 and IFN-γ secretion were quantified by ELISA. (G) PD-1 humanized C57BL/6 mice bearing MC38/hPD-L1 tumors were treated with HS636, Atezolizumab, or vehicle control (n = 10 for each group). The tumor volume was measured twice per week. (H) NCG mice bearing HCC827 tumors were injected with human PBMCs (1 × 107/mouse) and HS636 or isotype control hIgG1 (n = 6 for each group). The tumor volume was measured twice per week.