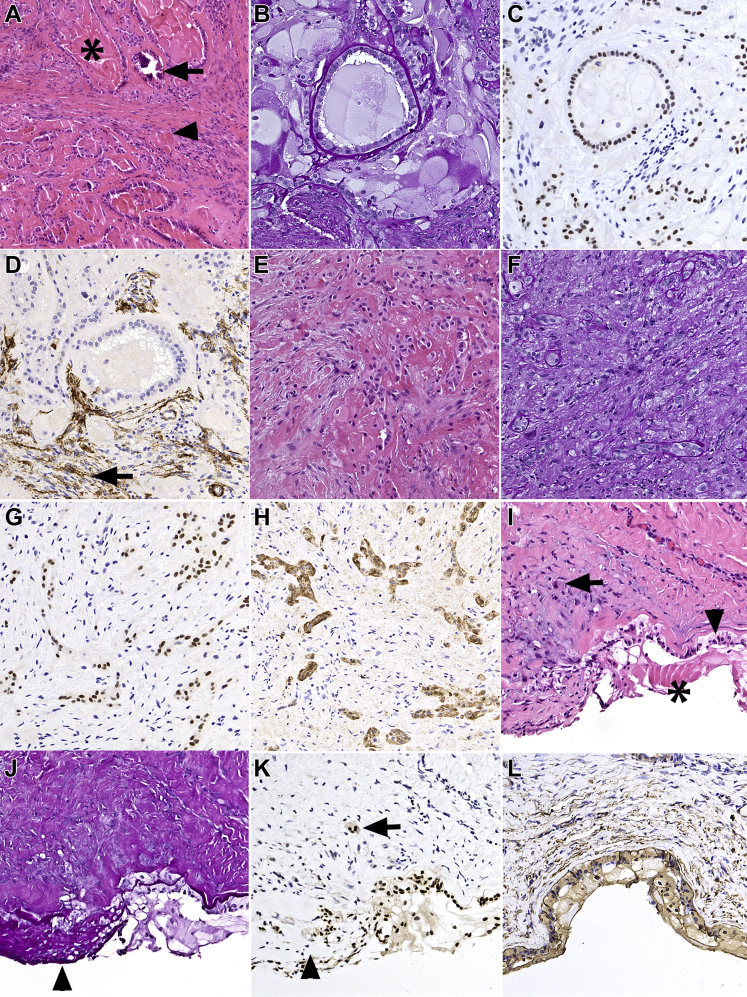
Figure 2.
Photomicrographs showing PAX8 expression in phakomatous choristoma and Peters anomaly with keratolenticular adhesion. A–H, Phakomatous choristoma. A, Phakomatous choristoma demonstrating characteristic islands composed of cataractous bladder cells (asterisk) and foci of dystrophic calcification (arrow) surrounded by cuboidal lens epithelium with thick lens capsule-like basement membrane material in a background of fibrotic stroma (arrowhead). B, Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) stain highlighting the thick basement membrane material reminiscent of lens capsule surrounding the cuboidal lens epithelium. C, Corresponding section showing a strong nuclear PAX8 expression in lens epithelium and bladder cells. The fibrotic stroma does not show positive stain results with PAX8. D, Focal positivity (arrow) of stromal component for smooth muscle actin (SMA), compatible with myofibroblastic differentiation reminiscent of anterior subcapsular cataract and capsular fibrosis. E, F, A region in phakomatous choristoma that lacks typical morphologic features and may present a diagnostic challenge with hematoxylin–eosin and PAS stains alone. G, Corresponding section stained with PAX8 highlighting bands and strands of lens epithelial cells that (H) coexpress S100. I–L, Peters anomaly with keratolenticular adhesion. I, Peters anomaly with keratolenticular adhesion demonstrating lens epithelium adherent to the posterior corneal surface (arrowhead) and focally entrapped in the fibrotic corneal stroma (arrow). Bladder cells also are present (asterisk). J, Corresponding PAS-stained preparation highlighting thick PAS-positive basement membrane material (lens capsule) overlying the cuboidal lens epithelium and PAS-positive material surrounding individual spindle cells (arrowhead), compatible with capsular fibrosis. K, Corresponding section stained with PAX8 highlighting the strong nuclear expression in the lens epithelium on the posterior corneal surface and entrapped in the corneal stroma (arrow). Nuclear staining also shows positive results in bladder cells, but is lost in the fibrous metaplasia of the lens epithelium (arrowhead). L, Vimentin shows positive results in the lens tissue and in the corneal stroma. Stains, hematoxylin–eosin (A, E, I), PAS (B, F, J), PAX8 (C, G, K), SMA (D), S100 (H), and vimentin (L); original magnifications, ×100 (A) and ×200 (B–L).