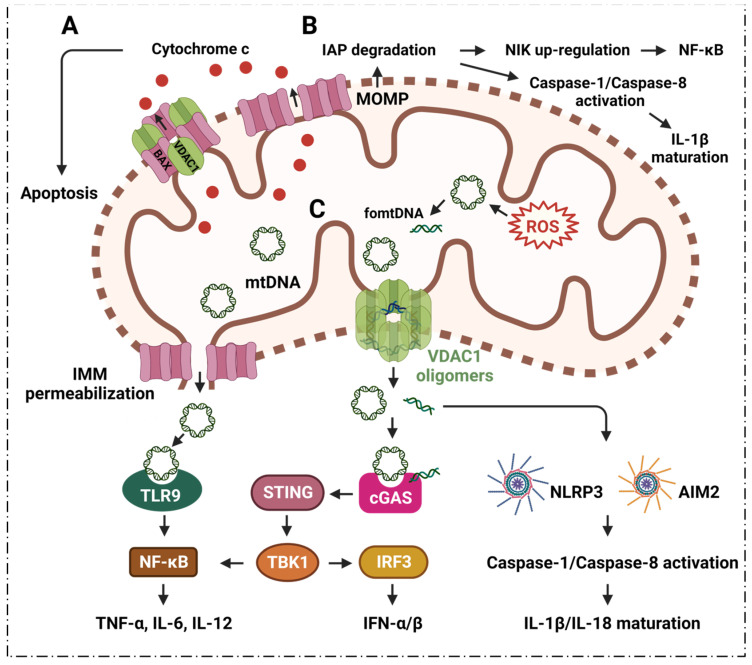
Figure 2.
VDAC1 mediates apoptosis and mtDNA release to promote cytokines expression and inflammatory pathogenesis. (A) Bcl-2 family member, BAX, interacts with VDAC1 to release cytochrome c into the cytoplasm, promoting apoptosis. (B) MOMP induces proteasomal degradation of IAPs, which causes NIK to further induce the pro-inflammatory NF-κB signal and activate caspase-1/8; this in turn results in the maturation of pro-inflammatory factor IL-1β. (C) Mitochondrial overproduced ROS oxidize mtDNA to fomtDNA. The mtDNA and fomtDNA pass the VDAC1 oligomers channel or the oligomerization BAX pore into the cytoplasm. The released mtDNA/fomtDNA induce the cGAS-STING pathway to promote interferon gene expressions via TBK1-IRF3 to up-regulate IFN-α/β, or through TBK1-NF-κB to enhance TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12. Additionally, mtDNA interacts with TLR9 and promotes TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12 expression via NF-κB signaling. Moreover, the released mtDNA induces the NLRP3 inflammasome and AIM2 inflammasome to enhance caspase-1/8 activation to promote IL-1β/IL-18 maturation. Abbreviations: AIM2: absent in melanoma 2; BAX: Bcl-2-associated X protein; cGAS: cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; Cyto c: cytochrome c; fomtDNA: oxidized mtDNA fragments; IAP: inhibitors of apoptosis; IFN: interferon; IL: interleukin; IRF3: interferon regulatory factor 3; IMM: inner mitochondrial membrane; MOMP: mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization; mtDNA: mitochondrial DNA; NF-κB: nuclear factor-κB; NIK: NF-κB induced kinase; NLRP3: nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat (LRR) containing P3; ROS: reactive oxygen species; STING: stimulator of interferon genes; TLR9: Toll-like receptor 9; TBK1: TANK-binding kinase 1; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; VDAC1: voltage-dependent anion channel 1.