Figure 4: IL-2R and IL-4R are principal hubs driving the expression of the atopy-associated module.
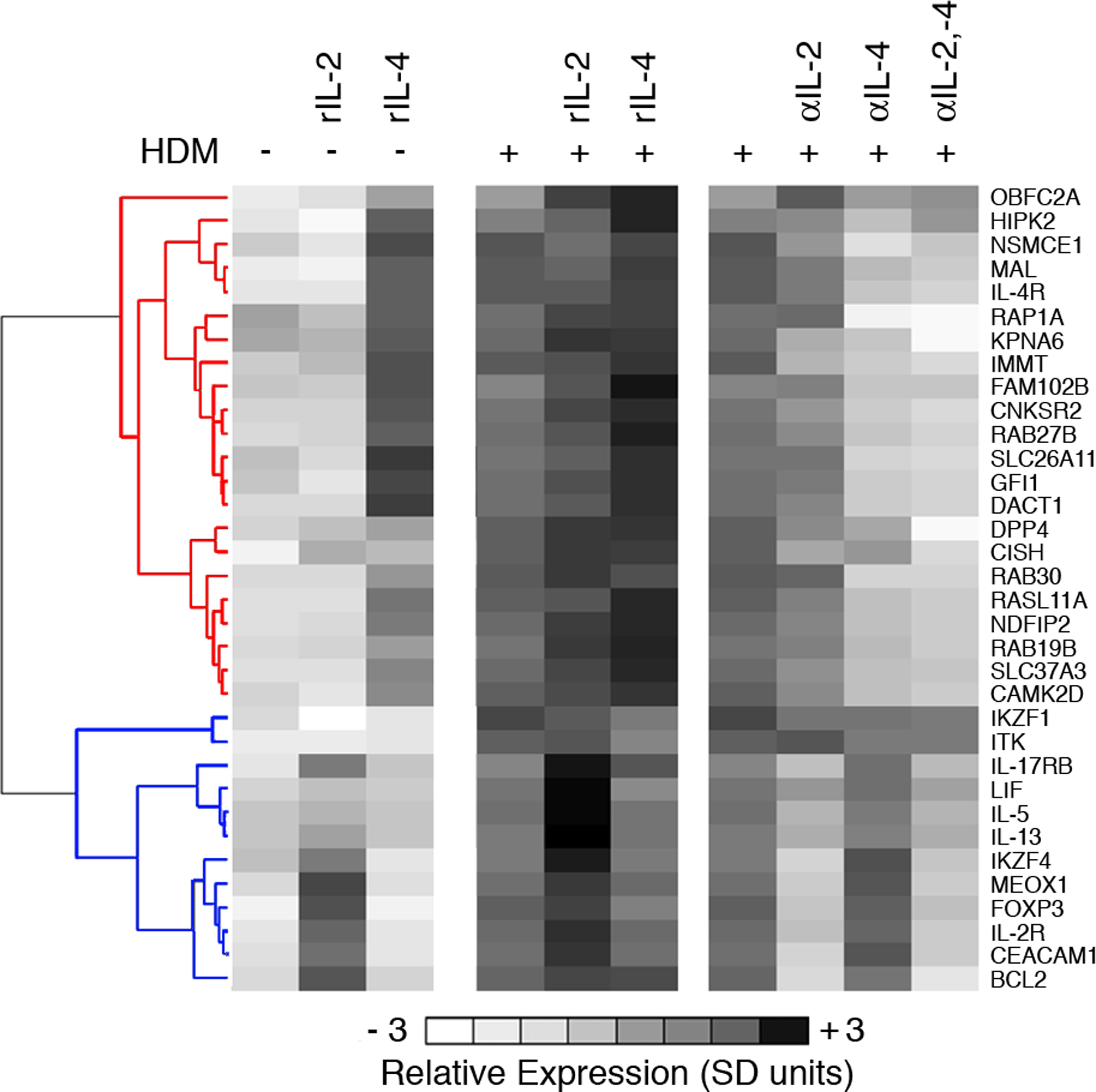
PBMC from HDM-sensitized atopics (n=8) were cultured in the presence (+) or absence (–) of HDM, recombinant IL-2 (rIL-2), recombinant IL-4 (rIL-4), or neutralizing antibodies against IL-2 (αIL-2), or IL-4 (αIL-4), or both (αIL-2, −4). At the termination of the 24 h cultures, CD4+ Th-cells were purified and expression of a subset of genes from the atopy-associated module was profiled by qRT-PCR. The qRT-PCR data were normalized to the stably expressed gene EEF1A1 (68), averaged across the subjects, mean centered (26), and scaled for unit variance (26). Hierarchical clustering (10) was performed on the genes to partition them into clusters of coexpressed genes. Two major expression patterns were identified; corresponding to genes that were regulated by IL-4 (red cluster dendrogram) or IL-2 (blue cluster dendrogram) genes. Detailed statistical analyses were also performed and are presented online in Table S4. Additional cultures were set up with appropriate isotype control antibodies and these did not substantively affect expression profiles (not shown). Abbreviations; SD, standard deviations.
