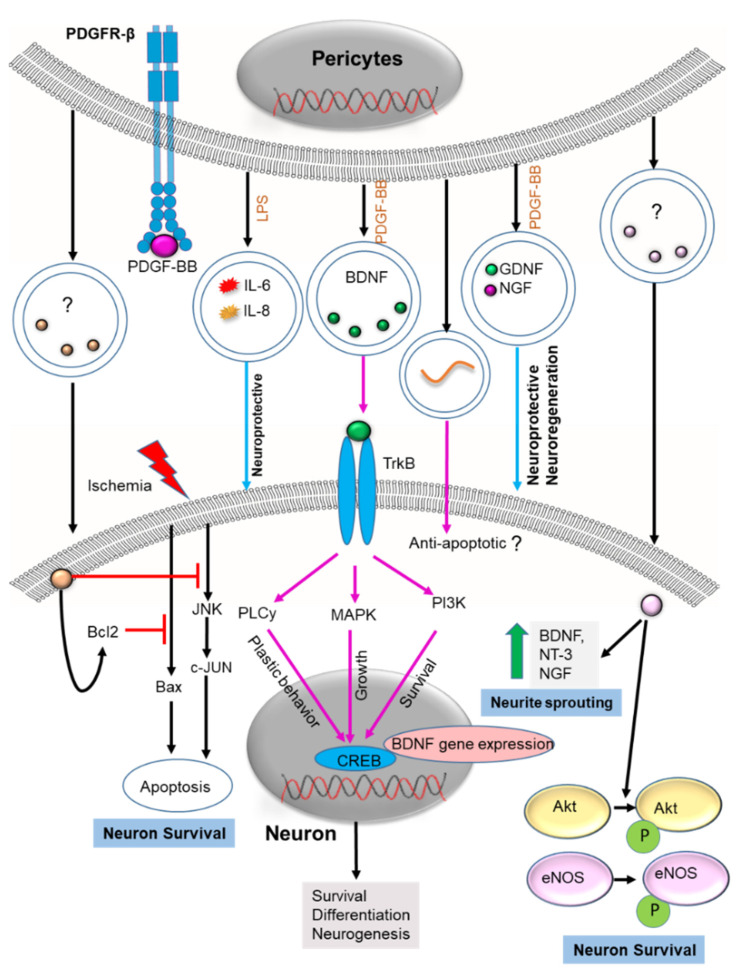
Figure 4.
Postulated mechanisms of PC-EVs in neuroprotection and neurogenesis. In response to PDGF-BB, PC-EVs release BDNF to recipient neurons. BDNF targets TrkB receptors and activates PLCγ, MAPK, and PI3K pathways to promote plasticity, growth, and survival. These pathways target CREB transcription factors, enhancing BDNF gene expression and promoting survival, differentiation, and neurogenesis. PC-EV release of growth factors such as GDNF, PTN, and NGF also protects against neurodegenerative pathology. PC-EVs enhance the expression of BcL2 for survival and inhibit both Bax apoptosis and the JNK/jun-c cell death pathway, thus promoting neuronal survival. PC-EVs released from pericytes also increase the expression of growth factors, including BDNF, NT-3, and NGF, which encourage neurogenesis. PC-EV phosphorylated Akt and eNOS promote neuronal survival. “?” indicates the content of the PC-EVs is not identified. Various miRNAs transferred to neurons may also promote neuronal survival and neurogenesis. “?” means the pathway is unknown. The black arrow indicates identified mechanism, the magenta arrow indicates the hypothesized Mechanism in PC-EVs based on the mechanism identified in other EVs, and the blue arrow indicates the speculative mechanism (miRNA: an acronym for micro RNA; PCs: pericyte; EVs: extracellular vesicles; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; NGF: nerve growth factor; GDNF: Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor; NT-3: Neurotrophin-3; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase; TrkB: Tropomyosin receptor kinase B; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor).