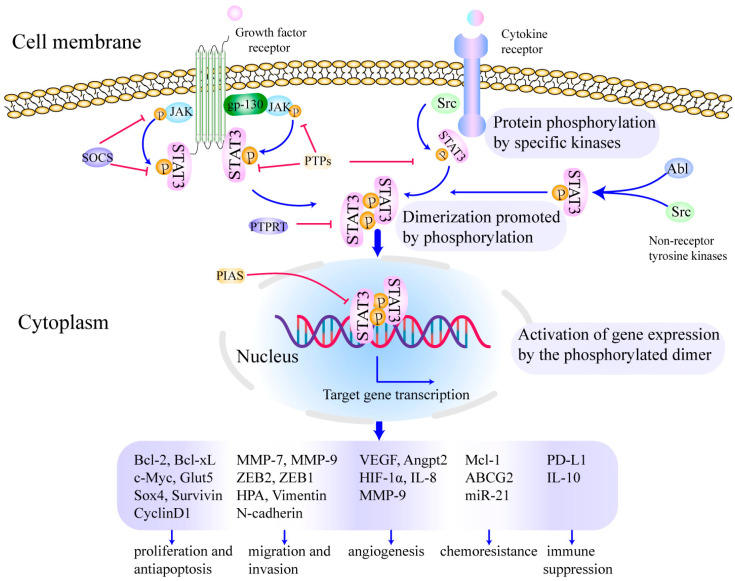
Figure 1.
Activation of STAT3 signaling promotes growth, metastasis, chemoresistance, immune suppression and angiogenesis in OSCC. The cytokines or growth factors bind to the corresponding receptors on the cell membrane, which further prompts STAT3 activation and subsequent regulates transcriptional activity. The whole process is divided into three steps as follows: (1) protein phosphorylation by specific kinases [19,26,27], (2) dimerization promoted by phosphorylation [51], (3) activation of gene expression by the phosphorylated dimer [52,53]. Finally, transcription and translation of the target gene regulate cell proliferation and anti-apoptosis, migration and invasion, chemoradiotherapy resistance and angiogenesis, as well as immune suppression in OSCC [22,54,55]. Reproduced/adopted in modified form from [56].