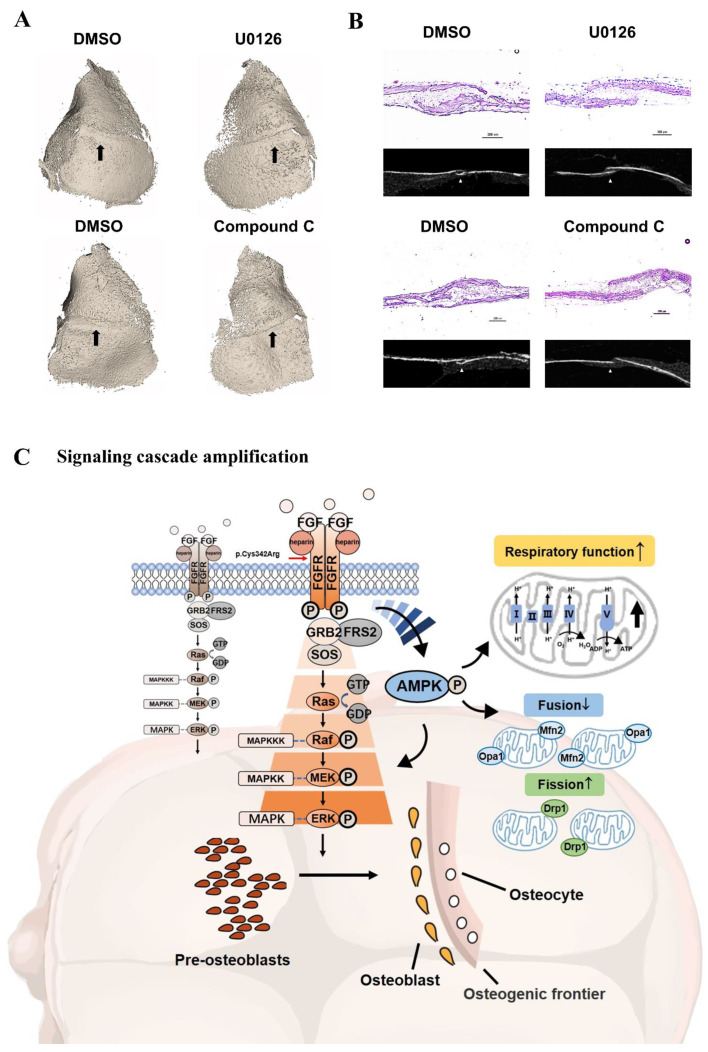
Figure 8.
(A) U0126 and Compound C attenuated the closure of coronal sutures of cultured calvarias. It was shown by 3D reconstruction images that there was an obvious linear gap between the frontal and parietal bone after the treatment with U0126 and Compound C. In the control groups, dense bony unions were formed in coronal suture regions. The coronal suture region was marked by a black arrow. (B) As shown by the section selected at the corresponding position of micro-CT, there were gaps between the osteogenic fronts of frontal and parietal bone in the inhibitor groups. The osseous cross-linking in the coronal suture was closer in control groups. As revealed by H&E staining, the synostosis between frontal and parietal bone presented as serrated in the control. However, there was a decreased overlapping region after treatment with U0126 and Compound C. (C) Schematic diagram of osteogenesis and internal mechanism. In the process of pre-osteoblast cells further differentiating, the relatively complete FGF/FGFR2-AMPK-Erk1/2 MAPK pathway plays a pivotal role. The constitutive activation of the AMPK-Erk1/2 signaling path network leads to enhanced osteogenesis because of the FGFR2 mutation (p.Cys342Arg) differing from wild-type FGFR2. In addition to being upstream of the Erk1/2 signal, the expression and activation of AMPK amplifies the mitochondria respiratory function and changes the ratio of mitochondrial division and fusion to respond to osteogenic activity. The differentiated osteoblasts then secrete the extracellular matrix and subsequently promote mineral deposition at the front edge of osteogenesis, which may lead to the malformation of cranial vault bones in Crouzon syndrome.