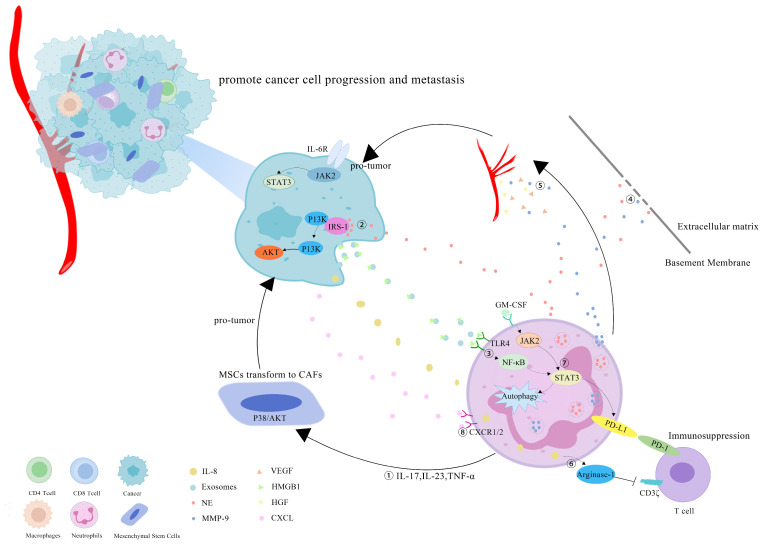
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of TANs that promote tumor progression: (1) TANs secrete cytokines, such as IL-17, IL-23 and TNF-α, to induce MSCs to convert into CAFs, and to promote tumor-cell proliferation; (2) TANs secrete NE to bind intracellular IRS-1, releasing its inhibitory effect on the PI3K/Akt pathway, and promoting tumor proliferation; (3) cell-derived exosomes induce the autophagy and N2 polarization of neutrophils via HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling to promote cancer-cell proliferation and migration; (4) TANs secrete NE and MMP-9 to degrade the ECM and accelerate the tumor invasion; (5) TAN-derived VEGF, HGF and MMP9 promote the angiogenesis of tumor cells; (6) tumor-derived IL-8 induces neutrophils to secret arginase-1, resulting in arginase depletion and the establishment of an immunosuppressive TME; (7) GM-CSF activates TANs to express high levels of the immunosuppressive molecule PD-L1 through the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway; (8) neutrophils can be recruited by tumor cells through chemokines, such as the CXCL/CXCR1/2 signal axis.