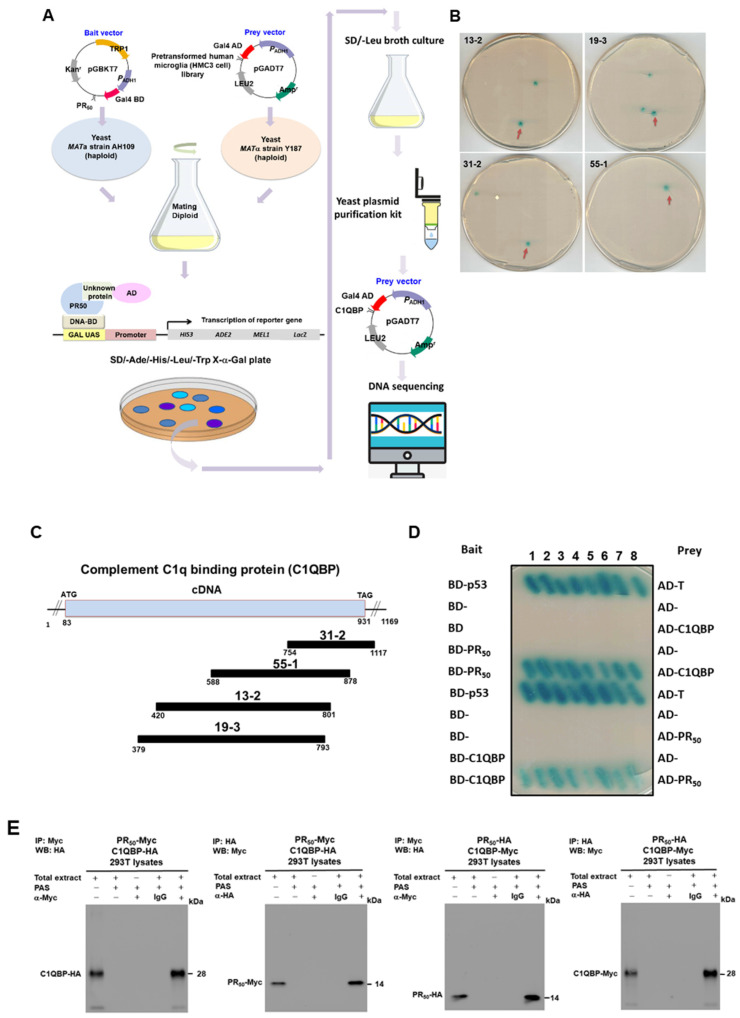
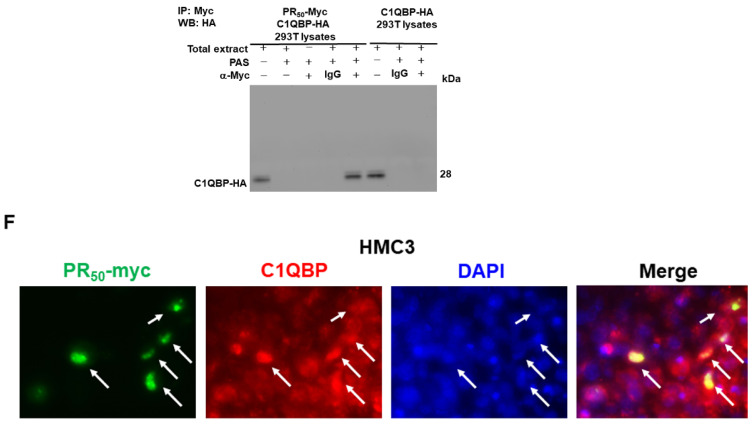
Figure 5.
Complement component 1 q subcomponent-binding protein (C1QBP) is one of the specific interaction partners of the PR50 protein. (A) The flowchart displays the yeast two-hybrid strategy for screening human HMC3 microglial cells’ cDNA library using PR50 as bait. (B) Clones in the screening plate containing the C1QBP fragment are shown (red arrows). Blue diploid cells contain four reporter genes that are activated in response to two hybrid interactions. (C) Schematic drawing of the overlapping C1QBP cDNA clones that span the coding region of the C1QBP gene (NCBI reference sequence: NP_001203). C1QBP contains a mitochondrial glycoprotein MAM33-like domain. (D) Confirming the interaction between PR50 and full length C1QBP using yeast two-hybrid assay. Diploid cells containing BD-p53 and AD-T were used as a positive control. (E) PR50 interacts with C1QBP in an immune co-precipitation (co-IP) analysis. 293T cells were co-transfected with pCMV-PR50-myc and pCMV-C1QBP-HA. The cells were then lysed and co-immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibody or anti-HA antibody, respectively. Finally, PR50 and C1QBP were identified on co-IP complexes with anti-HA antibody or anti-myc antibody by western blotting. Similarly, we co-transfected 293 T cells with pCMV-C1QBP-myc and pCMV-PR50-HA for co-IP. The cells were then lysed and co-immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody or anti-myc antibody, respectively. Finally, C1QBP and PR50 were identified on co-IP complexes with anti-myc antibody or anti-HA antibody by Western blotting. 293T cells were transfected with pCMV-C1QBP-HA as a negative control of co-IP. (F) PR50 (green) and C1QBP (red) are partially co-located in the nuclei of HMC3 cells by immunofluorescence staining analysis (white arrows). The nuclei were stained with DAPI.