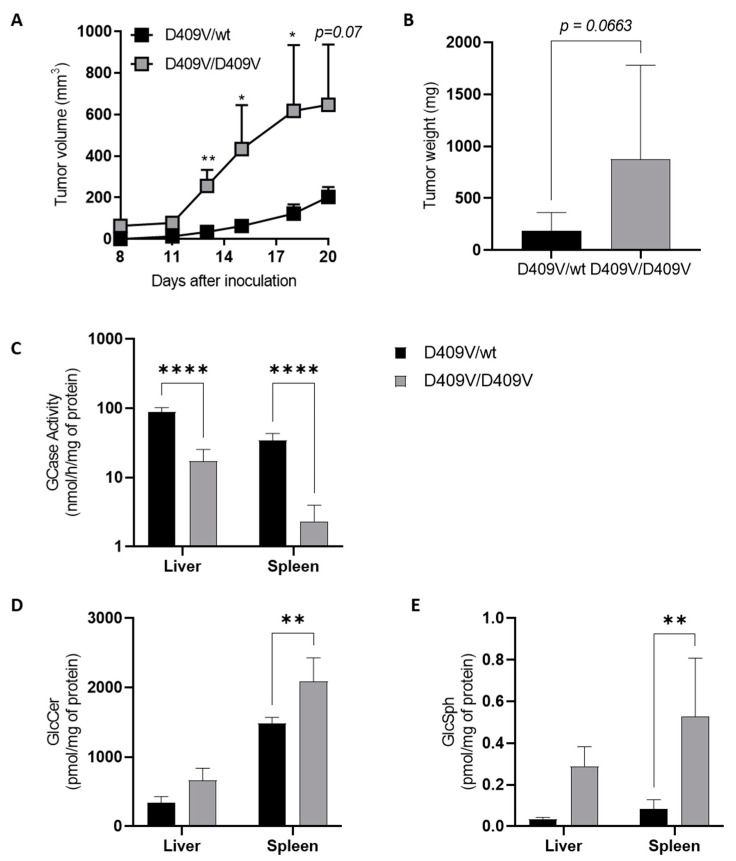
Figure 2.
Melanoma tumor growth is increased in a Gba1D409V/D409V Gaucher mouse model. Murine B16F10 melanoma cells (3 × 105) were injected subcutaneously into Gba1D409V/D409V (D409V/D409V) female mice and heterozygous (D409V/wt) littermates having the same mixed genetic background (19–22 weeks of age). (A) Tumor volumes were measured every 3 days. (B) Tumor weights were measured 25 days after tumor inoculation. Data are expressed as means +/− SEM of at least two independent experiments (n = 7–21 mice). (C) GCase enzyme activity was determined in lysates of liver and spleen isolated from D409V/D409V or heterozygous D409V/wt mice. Assays were performed in duplicate on samples of three to six animals. GlcCer (D) and GlcSph (E) were extracted by the Bligh and Dyer method [146] from the liver and spleen and analyzed by LC-MS (liquid chromatography coupled by mass spectrometry); assays were performed in duplicate on samples taken at day 20 of three to six animals (18–22 weeks of age). Statistical significance was determined by a Mann–Whitney test. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.0001.