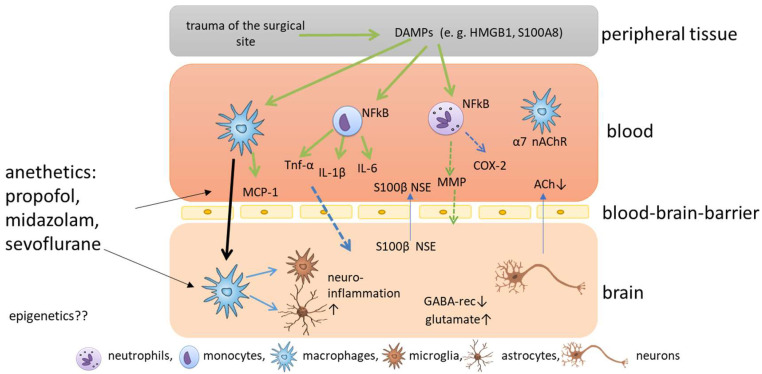
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the molecular mechanisms of postoperative cognitive impairment. Trauma of the surgical site causes the release of damage associated patterns (DAMPS), which are released into the blood where nuclear factor kappa B is activated in immune cells, such as neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages, which release cytokines and chemokines. The release of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2) cause permeabilization of the blood-brain barrier and pro-inflammatory cytokines and macrophages enter the brain. Here, microglia are activated and neuroinflammation is amplified.