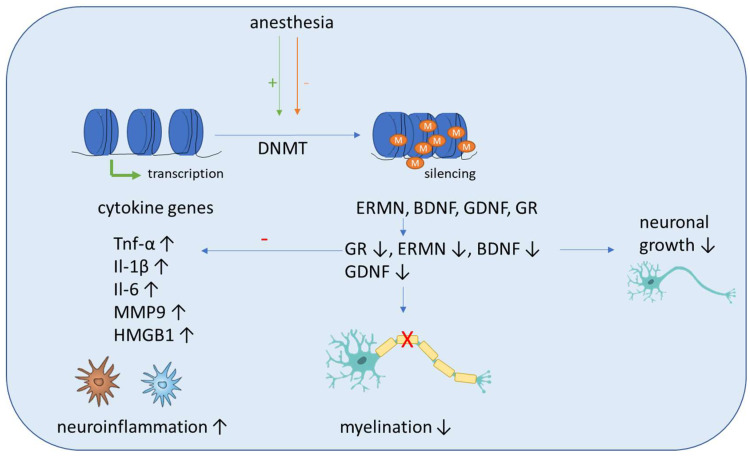
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the molecular mechanisms induced by anesthesia on DNA methylation. Anesthesia can cause both an increase and decrease of DNA-methyltransferase (DNMT) activity. The methylation of inflammatory genes (Tnf-α, IL-1β, Il-6, MMP9, HMGB1) is generally decreased, which leads to increased expression and aggravates neuroinflammation. Anti-inflammation is decreased by decreased expression of the anti-inflammatory transcription factor glucocorticoid receptor (GR). In addition, the methylation of genes associated with neuronal growth (BDNF, GDNF), differentiation and survival of existing neurons (ERMN) is increased, which reduces their expression and causes cognitive impairment due to demyelination and the reduced growth of neurons.