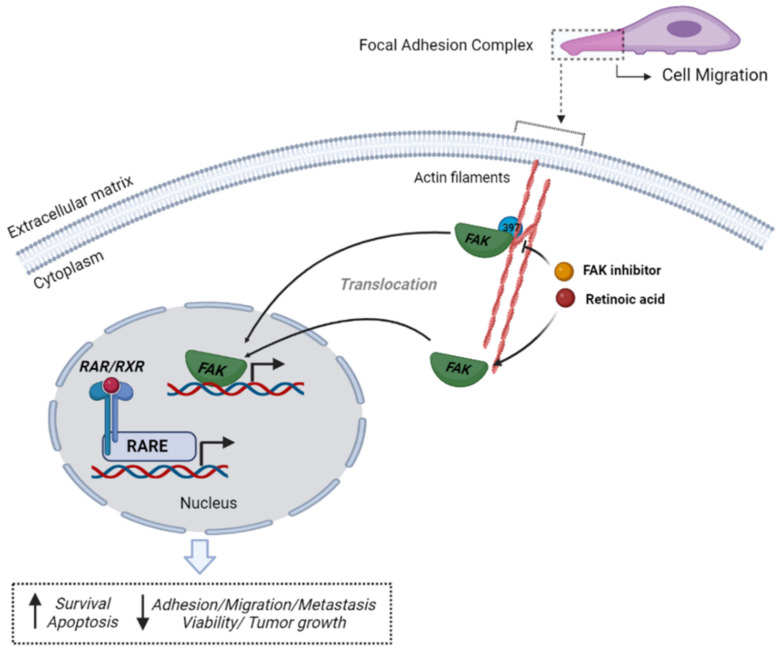
Figure 6.
Schematic figure of molecular changes triggered by RA plus FAKi in BC. Retinoic acid (RA) and FAK inhibitor (FAKi) induces FAK translocation from focal adhesion sites and cytoplasm to the nucleus. In the nucleus, FAK acts as a transcription factor in a kinase-independent manner. In parallel, RA binds to receptors RXR/RARs regulating the transcription of target genes. As result, cell detachment occurs blocking cell migration and reducing the metastatic process. Likewise, cell viability diminished due to apoptosis induction decreasing tumor growth and increasing mice survival. Figure created by BioRender.