Figure 3.
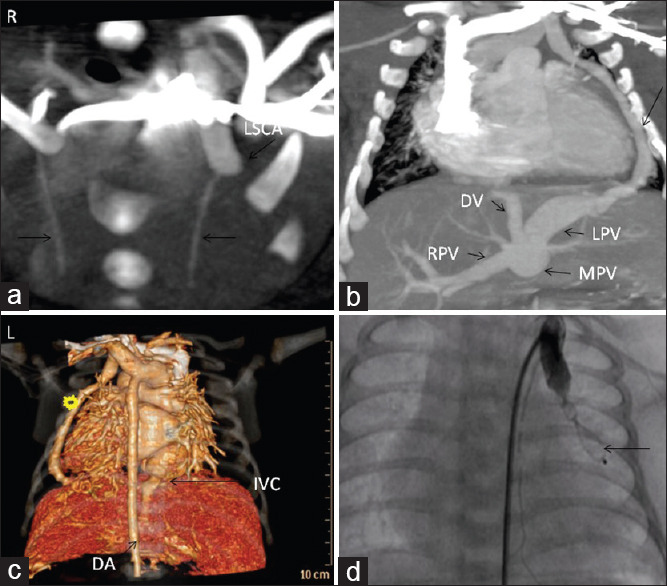
(a) Computed tomographic (axial plane) showing dilated proximal left subclavian artery (arrow) and normal calibre LIMA and RIMA. Right side has been identified as “R.” (b) Computed tomographic (coronal plane) showing the fistulous tract from the left subclavian artery, lateral to the left ventricle (arrow), piercing the diaphragm and joining the left portal vein. (c) Three-dimensional reconstruction of cardiac computed tomographic showing the separate diaphragmatic opening of the fistula and its distant relation to the inferior vena cava hiatus and descending aorta. (d) Contrast injection in the proximal left subclavian artery showing occlusion of the fistula by the ADO-II device (arrow) and LIMA arising normally from the dilated proximal left subclavian artery. MPV: Main portal vein; RPV: Right portal vein; DV: Ductus venosus.
