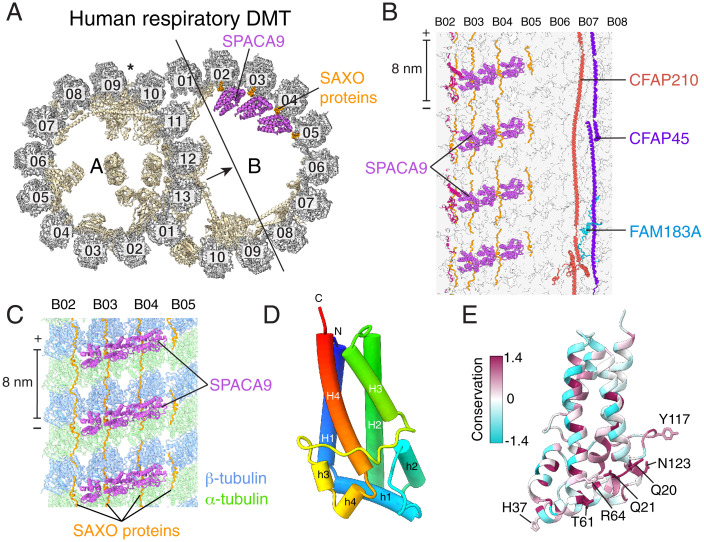
Fig. 3.
SPACA9 binds the B tubule of the respiratory doublet microtubule (DMT). (A) Cross section of the atomic model of the human respiratory DMT with tubulin colored gray, MIPs colored pale yellow, SPACA9 colored purple, and SAXO proteins colored orange. The arrow shows the direction of view in panel B. (B) Longitudinal section of the B-tubule atomic model viewed from the lumen showing striations of SPACA9 bound to protofilaments B02-B05 and other MIPs bound to protofilaments B06-B08. The polarity of the microtubule is shown at the ends of the scale bar. (C) SPACA9 binds at the intradimer interface between α- and β-tubulin and repeats with 8-nm longitudinal periodicity. (D) Atomic model of a single SPACA9 molecule with helices displayed as tubes and colored in rainbow from C- to N terminus. (E) Atomic model of SPACA9 colored by sequence conservation. Conserved residues are shown in magenta. Conserved residues that interact with tubulin and SAXO protein(s) are labeled.