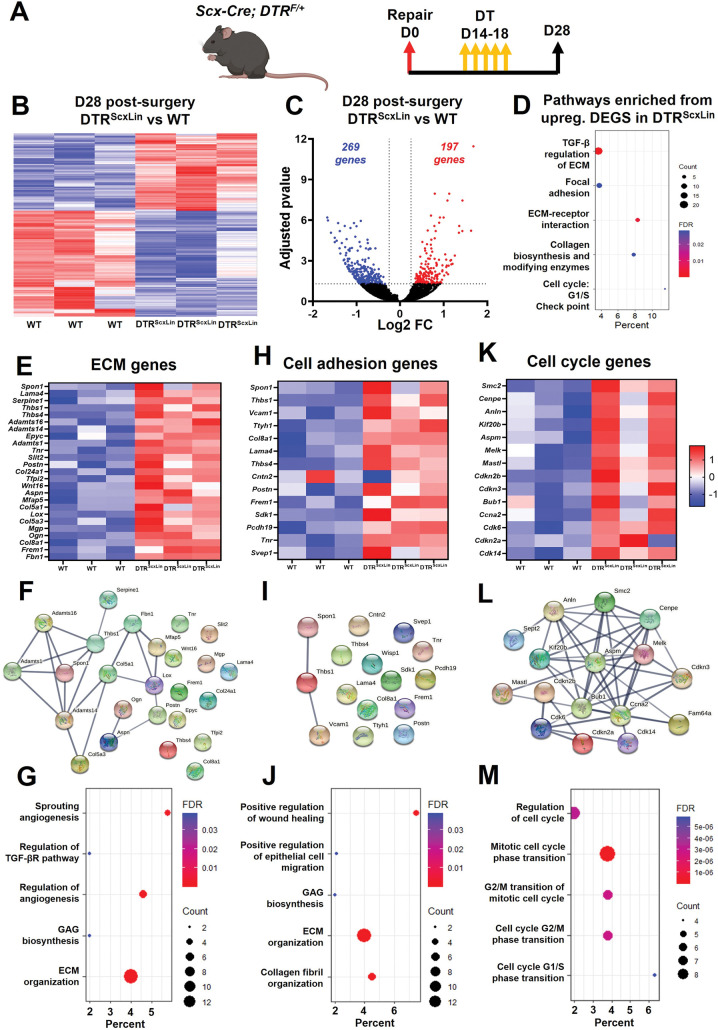
Fig 4. DTRScxLin tendons exhibit enriched biological pathways related to ECM synthesis and organization, cell-ECM receptor interaction, and cellular mitosis/proliferation.
A. Schematic of the mouse model used and timeline for tendon surgeries, DT injections, and tissue harvesting. B. Heatmap of all significantly different genes between D28 DTRScxLin and WT tendons. C. Volcano plot of all the significantly different genes between D28 DTRScxLin and WT tendons. D. Enriched biological pathways from the upregulated genes in D28 DTRScxLin relative to WT tendons. E. Heatmap with all the ECM (E), cell adhesion (F), and cell cycle (G) genes significantly upregulated in D28 DTRScxLin tendons. H. Protein-protein communication of all the ECM (H), cell adhesion (I), and cell cycle (J) genes significantly upregulated in D28 DTRScxLin tendons. N = 3 per genotype.