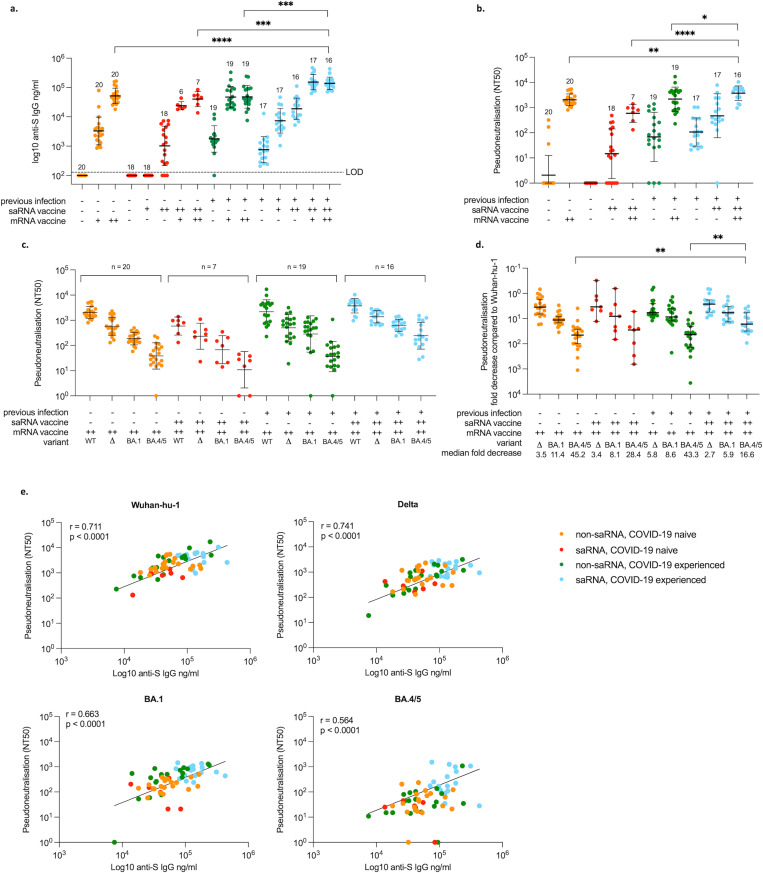
Fig 3. Binding and neutralising antibody responses.
3a. Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-hu-1 spike protein as measured by ELISA at baseline and two weeks following dose 1 and 2 of saRNA and mRNA vaccines in saRNA (COVAC1) participants (red and blue) and at baseline and two weeks following dose 1 and 2 of mRNA vaccines in non-saRNA participants (orange and green). 3b. Neutralising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-hu-1 measured using pseudovirus at baseline and two weeks following the 2nd dose of saRNA and mRNA vaccines in saRNA participants (red and blue) and two weeks following the 2nd dose of mRNA vaccine in non-saRNA participants (orange and green). 3c. Neutralising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-hu-1, Delta and Omicron BA.1 and BA.4/5 using pseudovirus two weeks following the second mRNA vaccine dose and the differences between groups. 3d. Fold decrease in neutralisation against Delta and Omicron BA.1 and BA.4/5 compared to Wuhan-hu-1 (y axis inverted) 3e. Correlation between binding antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-hu-1 spike protein (ELISA) and neutralisation (pseudovirus) against Wuhan-hu-1, Delta and Omicron BA.1 and BA.4/5 two weeks following the second mRNA vaccine dose. Number of samples included in the analysis indicated on graphs. Geometric mean titres (GMT) and standard deviation (sd) are shown. Differences between groups determined by Kruskall-Wallis and tested using Mann-Whitney. Median fold decrease within groups by Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank test. Correlations by Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. -, no exposure; +, single exposure; ++, two exposures; LOD, level of detection; WT, wildtype; Δ, Delta. Significant values displayed: **** p<0.0001; *** p<0.001; ** p<0.01; * p<0.05; ns, non-significant.