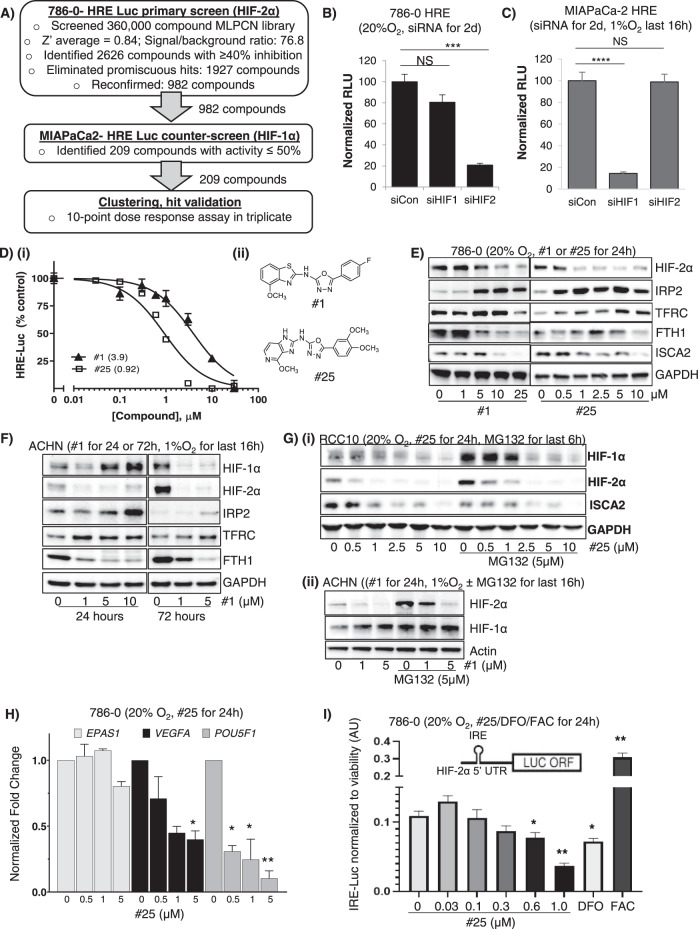
Fig. 1. Identification and characterization of novel HIF-2α selective inhibitors.
A Screening flow-chart for the identification of selective small molecule inhibitors of HIF-2α. B, C Validation of HIF-1α or HIF-2α dependency of a Hypoxia Responsive Element (HRE)-driven luciferase reporter construct stably expressed in (B) 786-0 or (C) MIAPaCa-2 cells. D (i) 786-0 HRE-Luciferase dose-response assays of indicated compounds (24-hour treatment) with IC50 values (μM) indicated in brackets; (ii) Chemical structures of compounds used in the study. E Western blots showing effects of treatment with #1 or #25 on levels of HIF-2α and other proteins in 786-0 cells in normoxia (20% O2). F Effects of 24- or 72-hours’ treatment with #1 in ACHN cells (exposed to hypoxia or 1% O2 for the final 24 h). G Effects of treatment of, (i) RCC10 cells with #25 ± proteasomal inhibitor, MG132 (5 μM 24 h, 20% O2), or of (ii) hypoxic ACHN cells with #1 ± MG132 (24 h, 1% O2) on HIF-1α and HIF-2α. H Quantitative RT-PCR showing effects of #25 on the transcription of HIF2A (EPAS1) and HIF-2 target genes VEGFA and OCT-3/4 (POU5F1). I Effect of #25 treatment on luciferase activity driven by a HIF-2α Iron-Responsive Element (IRE)-luciferase reporter construct stably expressed in 786-0 cells. The iron chelator, deferoxamine (DFO; 50 μM), and iron donor, ferric acetylcysteine (FAC; 25 µM) were used to confirm responsiveness of the reporter to iron perturbation. All data shown are representative of at least 2 independent experiments and show the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.