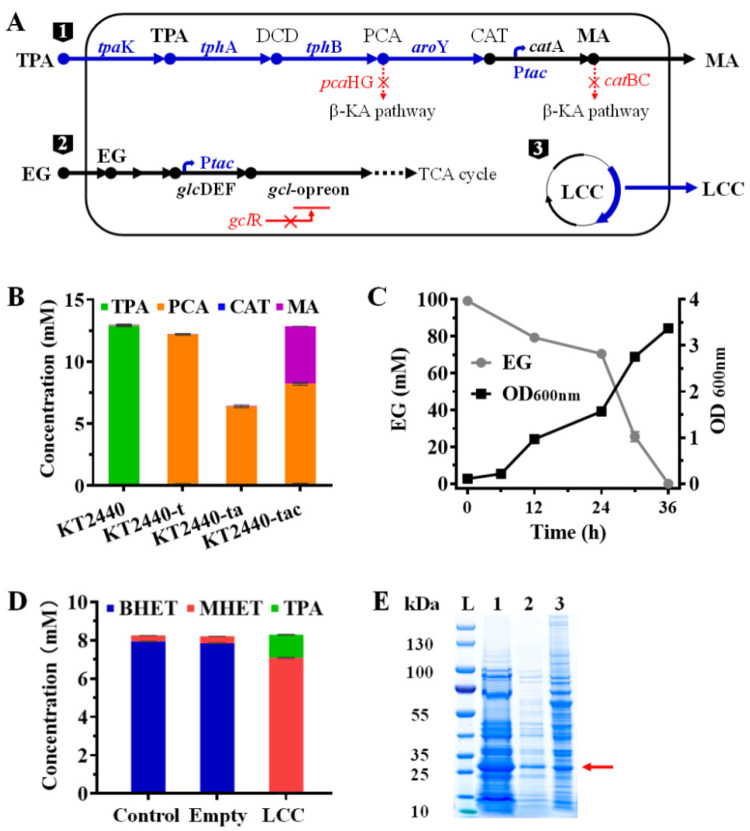
Figure 2.
Construction of a multifunctional strain. (A), P. putida KT2440 as the chassis for metabolic engineering design. 1, engineering the metabolic pathway for converting TPA to MA; 2, enhancing the endogenous EG metabolic pathway; 3, secretory expression of LCC on pBBR1MCS-2. (B), Bioconversion of TPA by the derived engineered strains in LB containing TPA. KT2440-t refers to the expression of tph-operon by replacing pcaGH in KT2440; KT2440-ta refers to the further expression of aroY-ecdB; KT2440-tac refers to the further deletion of catRBC and the promoter replacement of catA with tac promoter. (C), Growth and EG metabolism by P. putida KT2440-tacRD with the further deletion of gclR and the overexpression of glcDEF. (D), BHET hydrolysis by LCC crude enzyme from P. putida KT2440-tacRDL. Control refers to enzyme-free buffer and empty refers to crude enzyme from strain with an empty vector. (E), SDS-PAGE analysis of LCC crude enzyme from P. putida KT2440-tacRDL with the further expression of LCC. 1, Concentrated cell-free supernatant (10×); 2, cell-free supernatant; 3, cell lysis sample; TPA, terephthalate; DCD, 1,2-dihydroxy-3,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dicarboxylate; PCA, protocatechuate; CAT, catechol; MA, muconic acid; EG, ethylene glycol. TpaK, TPA transporter; TphA, TPA 1,2-dioxygenase; TphB, DCD dehydrogenase; AroY, PCA decarboxylase; CatA, CAT 1,2-dioxygenase; glcDEF, glycolate oxidase; gcl-operon, genes involved in glyoxylate carboligase metabolic pathway; gclR, the transcriptional regulator that represses the expression of gcl-operon; LCC, leaf-branch compost cutinase. Error bars indicate the standard deviation based on triplicate parallels.