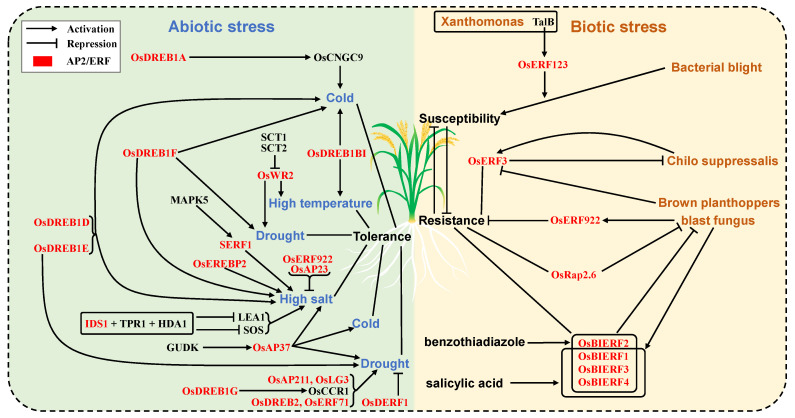
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of AP2/ERF transcription factors involved in abiotic and biotic stress regulation in rice. Left are the AP2/ERF regulatory networks of cold, high temperature, high salt and drought tolerance in rice; these factors are discussed in Section 3.8.1. OsDREB1A/D/E/F, OsDREB1BI and OsAP37 promote rice cold tolerance. OsDREB1BI and OsWR2 promote rice high temperature tolerance. OsDREB1E/F/G, OsDREB2, OsWR2, OsAP37, OsAP211, OsLG3 and OsERF71 promote rice drought tolerance, while OsDERF1 inhibits drought tolerance. OsDREB1D/E/F, SERF1, OsEREBP2, OsAP37 and IDS1 promote rice high salt tolerance, while OsERF922 and OsAP23 inhibit high salt tolerance. On the right, AP2/ERF genes participate in the regulation of disease and insect resistance in rice; these factors are discussed in Section 3.8.2. TalB, which is a transcriptional activator effector in Xanthomonas, promotes rice susceptibility to bacterial blight fungus X11-5A by promoting OsERF123. OsERF3 is activated by Chilo suppressalis attack, which improves rice resistance against chewing herbivores but is slightly suppressed by brown planthoppers attack. OsRap2.6 promotes rice blast fungus resistance, while OsERF922 inhibits rice blast fungus resistance. OsBIERF1/2/3/4 is involved in the rice blast defense response, and among them OsBIERF1/2/3/4 can be induced by benzothiadiazole, and OsBIERF1/3/4 can be induced by salicylic acid and blast fungus. The AP2/ERF transcription factors and other regulators are shown in red and black, respectively.