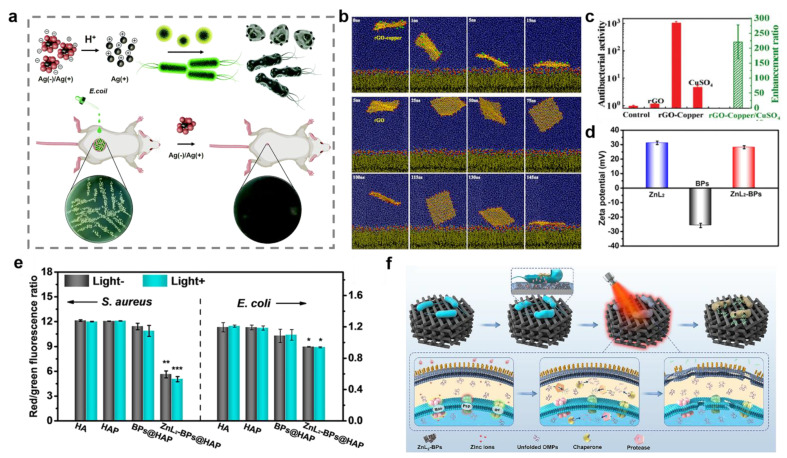
Figure 2.
Disruption of bacterial cell membranes through electrostatic interactions. (a) Schematic illustration for bacterial killing by acid-responsive Ag (−)/Ag (+) clusters. (b) Trajectory of binding between cell membrane and reduced graphene oxide (rGO)-copper composite and rGO. (c) Antibacterial activity (left axis) of rGO-copper composite and enhancement ratio (right axis) compared to copper ions. (d) Zeta potentials of zinc sulfonate ligand (ZnL2), black phosphorus nanosheets (BPs), and ZnL2-BPs. (e) Bacterial membrane potentials. * denotes p < 0.05, ** denotes p < 0.01, and *** denotes p < 0.001 compared with the hydroxylapatite (HA) group without near infrared (NIR)-irradiation. (f) The antibacterial mechanism of ZnL2-BPs@HAP. (d–f) Reprinted with permission from Ref [71]. Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society.