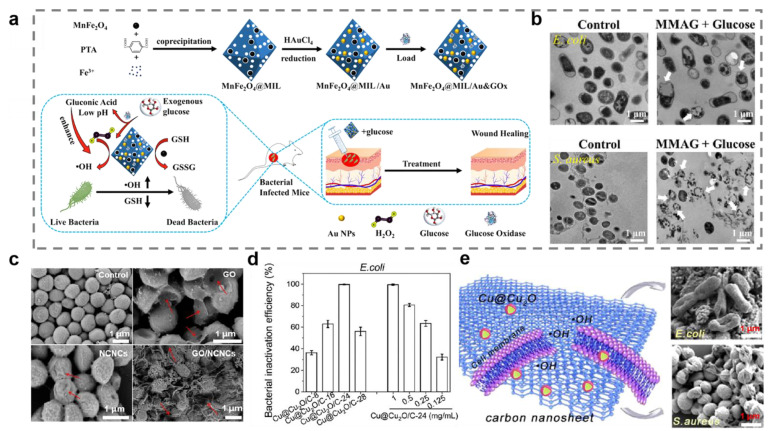
Figure 4.
Cell membrane damage caused by reactive oxygen species and sharp edges. (a) The preparation process and antibacterial mechanism of MnFe2O4@MIL/Au&GOx (MMAG). (b) Transmission electron microscope image of bacterial morphology. White arrows represent serious damage of bacterial cells. (c) The bacterial morphological changes with different treatments assessed by scanning electron microscope. Red arrows represent serious damage of bacterial cells. GO, graphene oxide; NCNC, nickel colloidal nanocrystal cluster. (d) Evaluation of antibacterial properties of carbon nanosheets decorated with core-shell Cu@Cu2O nanoparticles (Cu@Cu2O/C-24). (e) Schematic diagram of the antibacterial mechanism of Cu@Cu2O/C-24 under the dark condition. (a,b) Reprinted with permission from Ref. [74]. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society. (c) Reprinted with permission from Ref. [77]. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society. (d,e) Reprinted with permission from Ref. [79]. Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society.