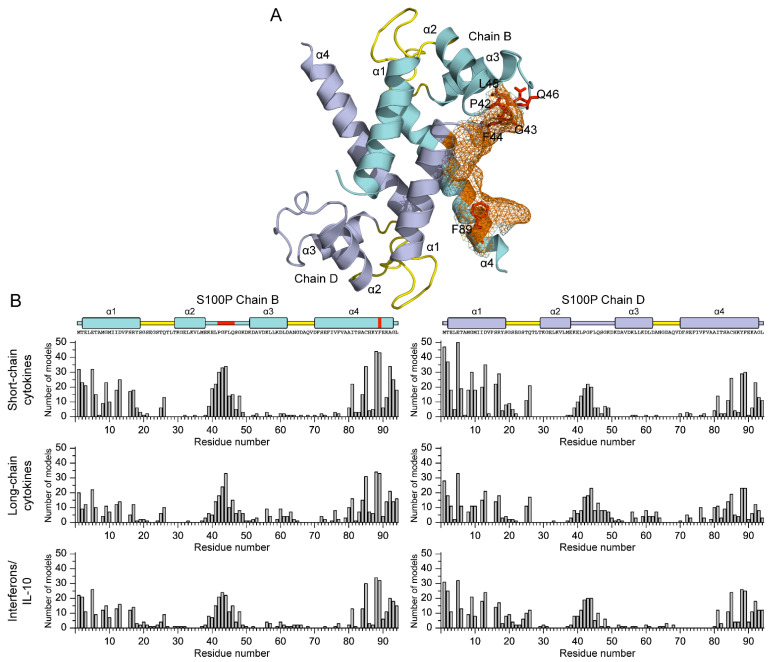
Figure 5.
(A) Tertiary structure of Ca2+-loaded S100P dimer (PDB entry 2MJW): chains B and D are highlighted in cyan and gray, respectively; the α-helices are labelled as α1-α4; the Ca2+-binding loops are yellow-colored. The residues predicted to constitute the cytokine-binding site are shown as orange mesh surface: residues P42, G43, F44, C85, Y88, and F89 (chain B), and residues M1 and E5 (chain D). The residues P42, G43, F44, L45, Q46, and F89 (see Table 4) of chain B are depicted as red balls and sticks. (B) Distributions of the predicted contact residues of Ca2+-loaded S100P dimer over its amino acid sequence within models of S100P complexes with representatives of specific families of four-helical cytokines (see Table S4). Ten docking models were taken into account for each S100P–cytokine pair. The boundaries of secondary structure elements of S100P were taken from PDB entry 2MJW; the residues P42, G43, F44, L45, Q46, and F89 (see Table 4) of chain B are indicated in red.