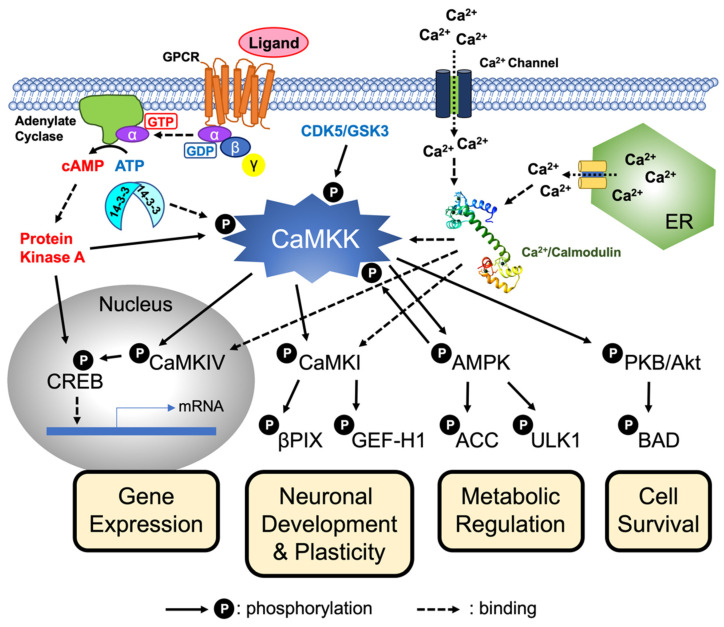
Figure 3.
CaMKK-mediated cellular signaling. Increasing intracellular Ca2+ concentration triggers the Ca2+/CaM-dependent activation of CaMKK, resulting in the activation of the downstream protein kinases including CaM-kinase I (CaMKI), CaM-kinase IV (CaMKIV), AMPK (5′AMP-kinase), and protein kinase B (PKB/Akt) through the phosphorylation of their activation-loop Thr residues. The CaMKK-mediated phosphorylation cascade is involved in a wide variety of physiological functions including transcriptional activation, neuronal development and plasticity, metabolic regulation, and cell survival. CaMKK is regulated by multiple cellular signaling cascades, such as intracellular Ca2+, cAMP/PKA signaling, 14-3-3-binding, feedback phosphorylation by activated AMPK, and cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (CDK5)/glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3)-mediated phosphorylation. Modified from Ref. [68]. Cream yellow boxes indicate physiological functions of CaMKK-mediated signaling pathways. CREB; cAMP-response element binding protein, βPIX; Pax-interacting exchange factor β, GEF-H1; guanine nucleotide exchange factor H1, ACC; acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ULK1; Unc51-like-kinase 1, and BAD; BCL2 associated agonist of cell death.