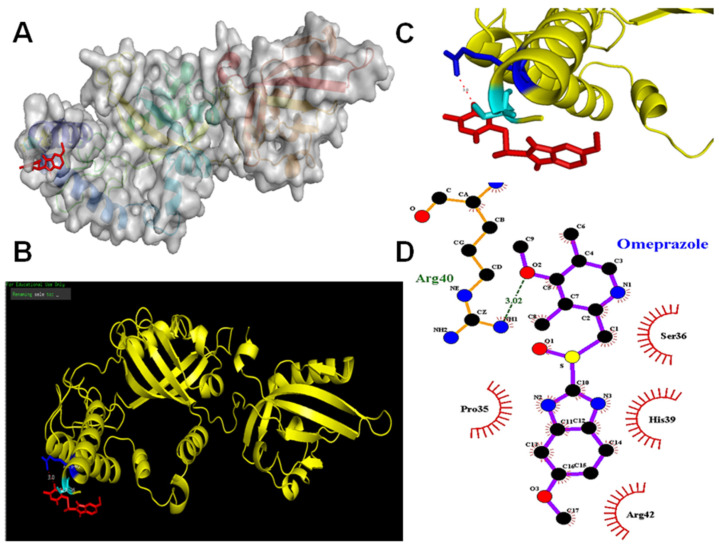
Figure 3.
Omeprazole activated the AhR (Ser36) site by a molecular docking simulation. The chemical structure of omeprazole revealed binding modes in the AhR (Ser36) site by virtual screening. General and local overviews of the best interaction after automated docking of binding omeprazole (red) to the active site of AhR are shown. (A) Surface representation of the ligand–receptor binding. Omeprazole (red) and AhR are shown in surface representation. (B) Local interaction positions of the AhR (Ser36) active site (blue). The cave entrance of the zoom-in binding mode of AhR and omeprazole (red) is shown. (C) The molecular structure of human AhR with Ser 36 is depicted as a ribbon diagram, with helices and loops. A molecular surface representation of the binding mode of AhR and omeprazole is shown targeting Ser36 representation. The 3D representation of the interactions of omeprazole binding to the AhR active site was generated by PyMOL. (D) LIGPLOT generates schematic diagrams of 2D ligand–protein interaction diagrams. The interactions shown are those mediated by hydrogen bonds and by hydrophobic contacts.