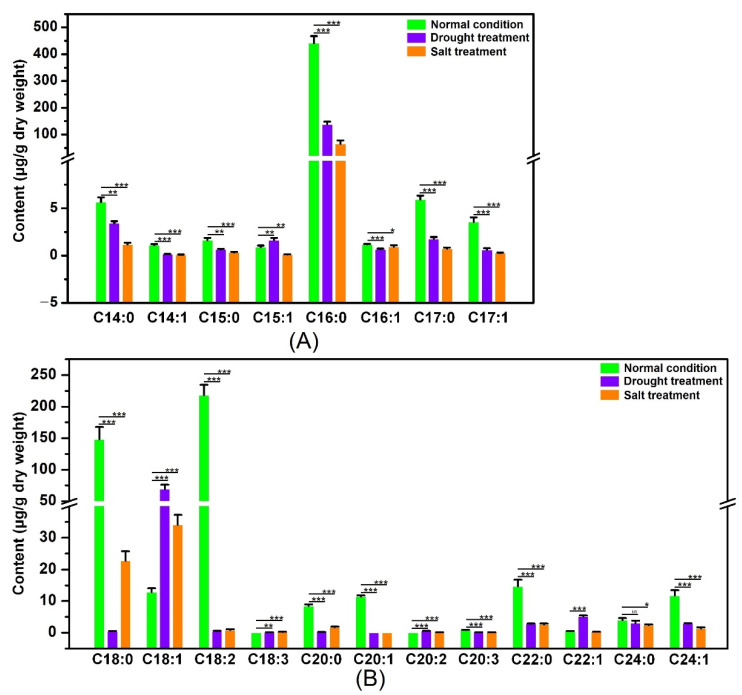
Figure 10.
The gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis of the SFA and UFA contents of poplar leaves before and after drought or salt stress. (A) The contents of C14-C17 SFAs and UFAs in poplar leaves cultivated under normal conditions and drought or salt stress. (B) The contents of C18-C24 SFAs and UFAs in poplar leaves cultivated under normal conditions and drought or salt stress. Three biological replicates were performed per group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared to control poplar. The kinds of SFAs and UFAs included myristate (C14:0), cis-9-tetradecenoate (C14:1), pentadecanoate (C15:0), cis-10-pentadecenoate (C15:1), palmitate (C16:0), palmitoleate (C16:1), margarate (C17:0), cis-10-heptadecenoate (C17:1), octadecanoate (C18:0), oleate (C18:1), linoleic acid (C18:2), linolenic acid (C18:3), icosanoate (C20:0), eicosenoate (cis-11) (C20:1), eicosadienoate (cis-11, 14) (C20:2), eicosatrienoate (cis-8,11,14) (C20:3), behenate (C22:0), erucate (C22:1), lignocerate (C24:0), and nervate (C24:1).