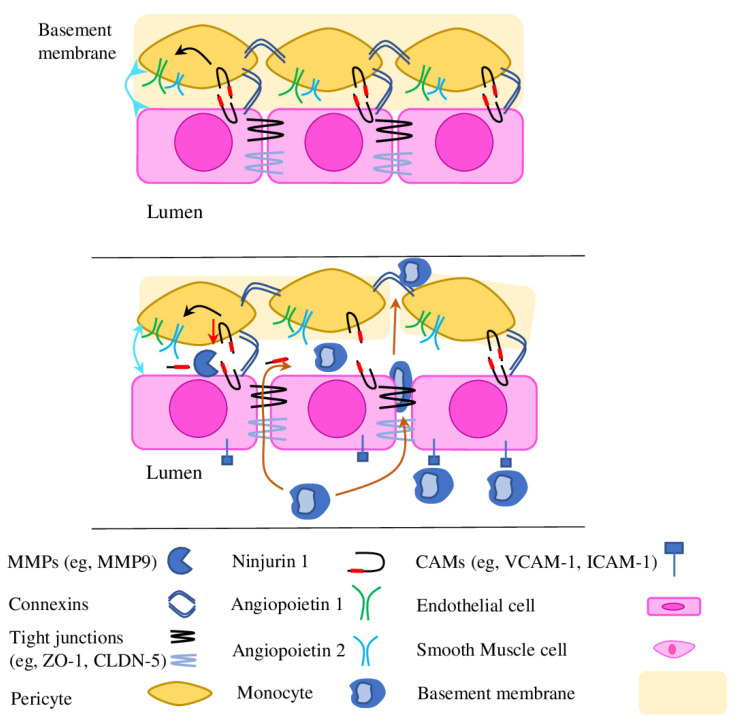
Figure 3.
The role of adhesion molecules in pericyte–pericyte and pericyte–ECs communication. Disruption of the PC/PC and PC/EC signalling causes a wide variety of changes: (1) pericyte loss; (2) EC activation and extravasation of immune cells (orange arrows); (3) MMP activation leads to loss of tight and gap junctional proteins (occludens, claudins and connexins) and Ninj1 cleavage, changes in cells’ organisation and widening EC/EC junctional gaps, disrupting PC/PC connection and PC/EC association (cyan arrows); (4) MMP9 degrades basement membrane, which facilitates further PC loss and EC desquamation, morphologic changes to ECs with cellular hyperplasia and aberrant angiogenesis. The level of Ninj1 expression regulates Ang proteins expression (black arrows) and, subsequently, EC/PC association.