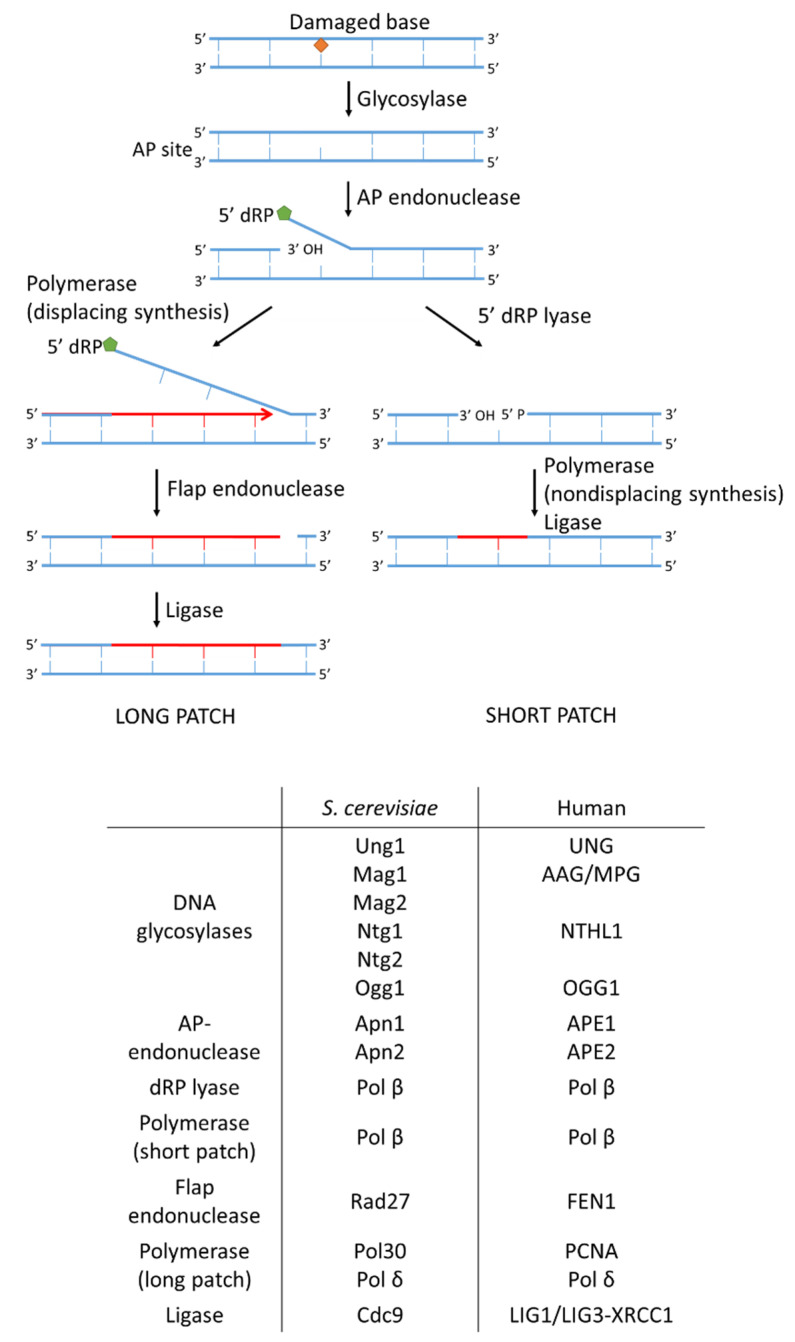
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of base excision repair (BER), mismatch repair (MMR), and nucleotide excision repair (NER). (A) Mechanism of BER. The base lesion is recognized and removed by DNA glycosylases. The resulting apuric or apyrimidic (AP) site is processed by AP endonucleases. In a long patch, BER displacing synthesis is followed by flap removal by Rad27, and ligation takes place. In a short patch, BER deoxyribose phosphate (dRP) lyase excises one nucleotide, which is followed by gap filling and ligation.