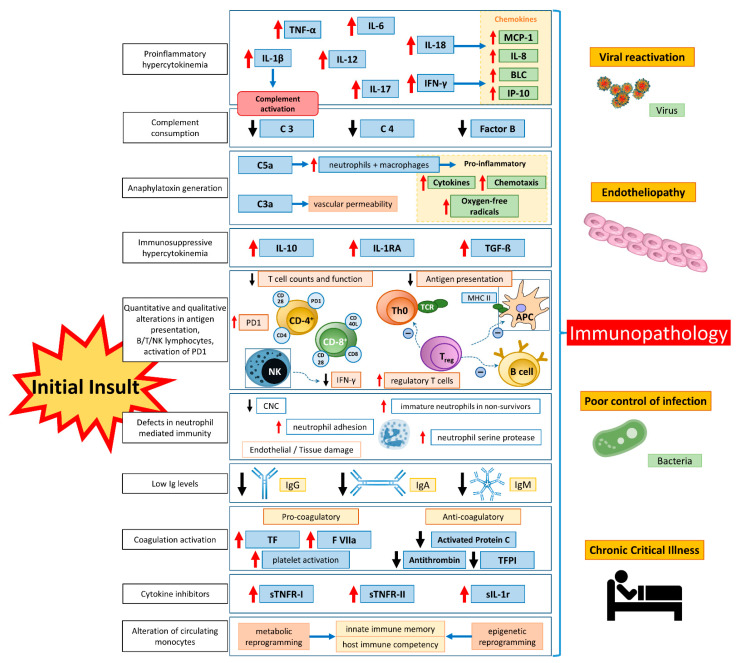
Figure 1.
Aspects of immunological dysfunction caused by sepsis with details of the entities involved. APC, antigen-presenting cell; BLC, B-lymphocyte chemoattractant; CD, cluster of differentiation; CNC, critical neutrophil concentration; IFN-y, interferon y; Ig, immunoglobulin; IL, interleukin; IP-10, IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MHC II, major histocompatibility complex II; PD1, programmed death protein 1; sIL-1r, soluble interleukin-1 receptor; sTNFR, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor; TCR, T-cell receptor; TF, tissue factor; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β. Adapted from Bermejo-Martin JF with permission [151].