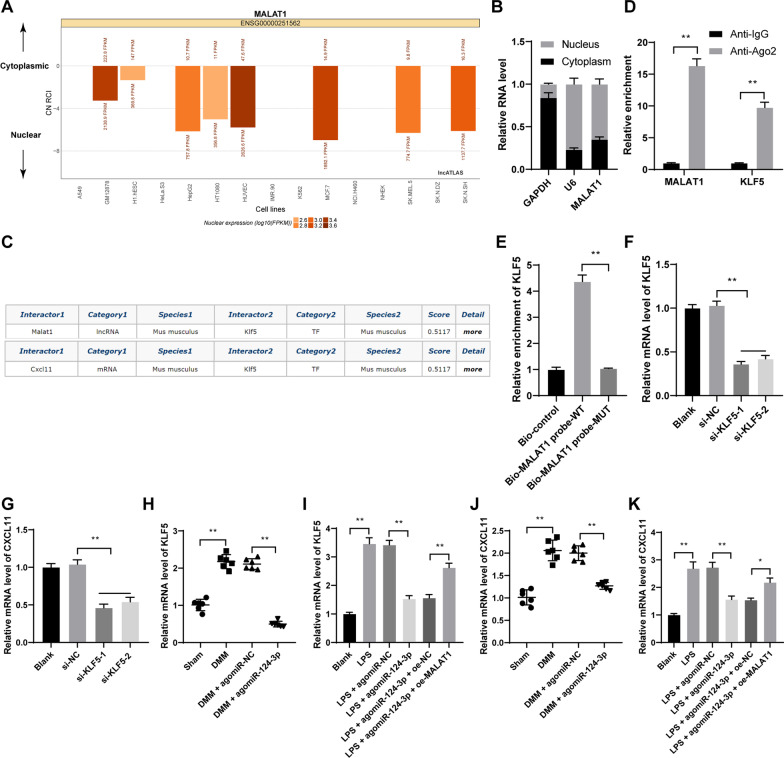
Fig. 5.
MALAT1 binds to transcription factor KLF5 to promote CXCL11 transcription. A, the subcellular localization of MALAT1 was predicted via the LncATLAS website. B, fractionation of nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA verified that MALAT1 was mainly localized in the nucleus. C, The binding relations between MALAT1 and KLF5 and between KLF5 and CXCL11 were predicted through the RNAInter database. D and E, the binding relation between KLF5 and MALAT1 was verified by RIP assay (D) and RNA pull-down assay (E). si-KLF5-1 or si-KLF5-2 was transfected into cells to downregulate KLF5 expression, with si-NC as the control. F, KLF5 transfection efficiency was verified by RT-qPCR. G, CXCL11 expression in cells with si-KLF5 was detected by RT-qPCR. H and I, KLF5 expression in tissue (H) and chondrocytes (I) were determined by RT-qPCR. J and K, CXCL11 expression in tissue (J) and chondrocytes (K) were determined by RT-qPCR N = 6, cell experiments were repeated 3 times independently. Data in panels B, D, E–G, I, and K were presented as mean ± standard deviation. Two-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data in panel D, and one-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data in panels E–K. Tukey's multiple comparisons test was applied for the post hoc test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01