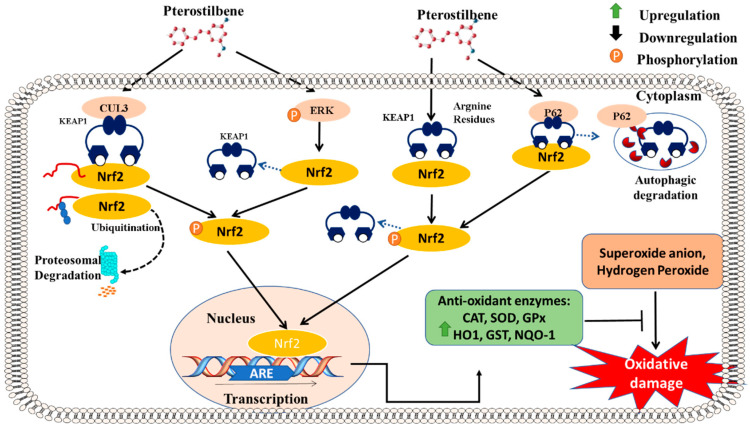
Figure 1.
Nrf-2-mediated antioxidant pathway of pterostilbene: Activation and phosphorylation of Nrf-2 signaling is the major mechanism through which the antioxidative response is induced by PTS. Ubiquitination mediated by Cullin-3 (CUL-3) leads to the proteasomal degradation of Nrf-2. PTS inhibits the ubiquitin–proteasome system, thereby increasing the accumulation of Nrf-2. PTS also enables the phosphorylation of Nrf-2, which is critical in the nuclear translocation of the transcription factor. Moreover, PTS phosphorylates and activates the ERK signaling pathway, which mediates the dissociation of Keap-1, resulting in Nrf-2 activation. Furthermore, PTS stimulates the binding of Keap-1 and p62, which enhances the activation of Nrf2. Following its activation and nuclear translocation, Nrf-2 binds to ARE and induces the expression of antioxidant enzymes, which in turn critically attenuate oxidative damage in host cells.