Table 1.
Toxic effects of different fungal toxins and protective effects and mechanisms of quercetin.
| Fungi | Fusarium | Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus parasiticus | Aspergillus ochratoxin, Aspergillussulphureus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mycotoxins | Deoxynivalenol (DON) | Zearalenone (ZEN) | Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) | Ochratoxin A (OTA) |
| Structure |
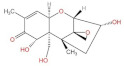
|
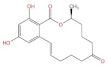
|
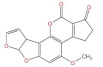
|
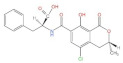
|
| Main area of action | Gastrointestinal and immune system | Reproductive organs | Liver, spleen, kidney | Liver, kidney |
| Main toxic effects | Fine cell and body fluid mediated, inhibition of protein synthesis | Lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial pathway, and DNA damage | Mutagenic, deformogenic, and carcinogenic | Hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, teratogenicity, and immunosuppression |
| Protective effect of quercetin | Protects caco-2 cells from damage | Protects HEK293 and HCT116 cells and inhibits apoptosis | Improves the brain, enhances learning and memory, inhibits biotransformation of AFB1, and delays degenerative neurological diseases | Protects cells from damage |
| Protective mechanism of quercetin | Inhibits the production of ROS and increases cellular activity | Inhibits ROS production, antioxidant activity, and reduces ER256 levels | Increases GSH levels, competes with AFB1 for binding sites, increases glutathione peroxidase levels, increases oxidative dismutase activity, and reduces lipid peroxidation reaction | Activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and reduction of ROS levels |
| References | [24,25,35] | [54,55,56,57] | [37,39,40,42,44] | [50,58] |
