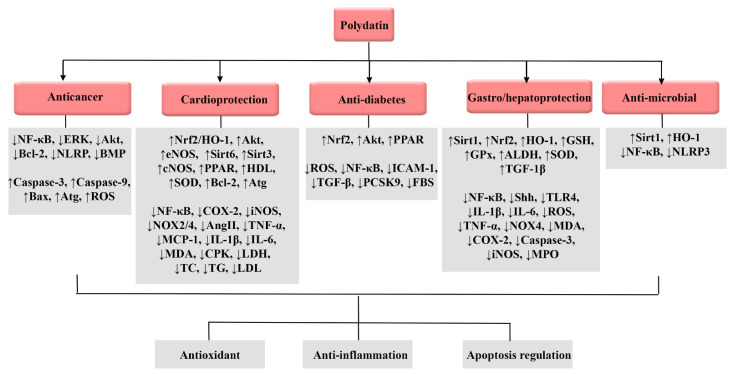
Figure 2.
Therapeutic targets of polydatin against cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, gastric/hepatic failure, and infection. ADH: alcohol dehydrogenase, Akt: protein kinase B, ALDH: aldehyde dehydrogenase, ALT: alanine transaminase, AST: aspartate transaminase, Atg: autophagy-related gene, Bax: Bcl-2-associated x, Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma 2, BMP: bone morphogenetic protein, CAT: catalase, cNOS: constitutive nitric oxide synthase, COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2, CPK: creatine phosphokinase, eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase, FBS: fasting blood sugar, GSH: glutathione, GPx: glutathione peroxidase, HDL: high-density lipoprotein, HO-1: heme oxygenase-1, ICAM-1: intercellular adhesion molecule-1, IL: interleukin, iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase, LDH: lactate dehydrogenase, LDL: low-density lipoprotein, MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, MDA: malondialdehyde, MPO: myeloperoxidase, NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa B, NO: nitric oxide, NOX: NADPH oxidase 4, NLRP3: nucleotide-binding domain (NOD)-like receptor protein 3, NOS: nitric oxide synthase, Nrf2: nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, PCSK9: proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type-9, PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor, PBEF: pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor, ROS: reactive oxygen species, Shh: Sonic hedgehog, Sirt: sirtuin, SOD: superoxide dismutase, TC: total cholesterol, TFEB: transcription factor EB, TG: triglyceride, TGF-β: transforming growth factor-beta1, TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α.