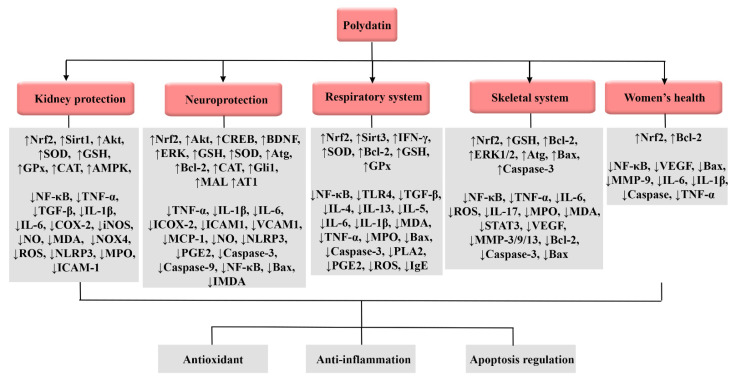
Figure 3.
Therapeutic targets of polydatin against kidney injury, neurodegeneration, respiratory dysfunction, skeletal problems, and women’s disorders. Akt: protein kinase B, AMPK: adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase, Atg: autophagy-related gene, Bax: Bcl-2-associated x, Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma 2, BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor, CAT: catalase, COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2, CREB: cAMP response element-binding proteins, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase, GSH: glutathione, GPx: glutathione peroxidase, ICAM-1: intercellular adhesion molecule-1, IgE: immunoglobulin E, IL: interleukin, INF-γ: interferon-γ, iNOS: inducible nitric oxide, MALAT1: metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1, MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, MDA: malonaldehyde, MMP: matrix metalloprotease, MPO: myeloperoxidase, NO: nitric oxide, NF-κB: nuclear factor-kappa B, NOX4: NADPH oxidase 4, NLRP3: nucleotide-binding domain (NOD)-like receptor protein 3, Nrf2: nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, PGE2: prostaglandin E2, PLA2: phospholipase A2, RANKL: receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa Β ligand, ROS: reactive oxygen species, SOD: superoxide dismutase, STAT: signal transducer and activator of transcription, TGF-β1: transforming growth factor-beta1, TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α, CAM-1: vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor.