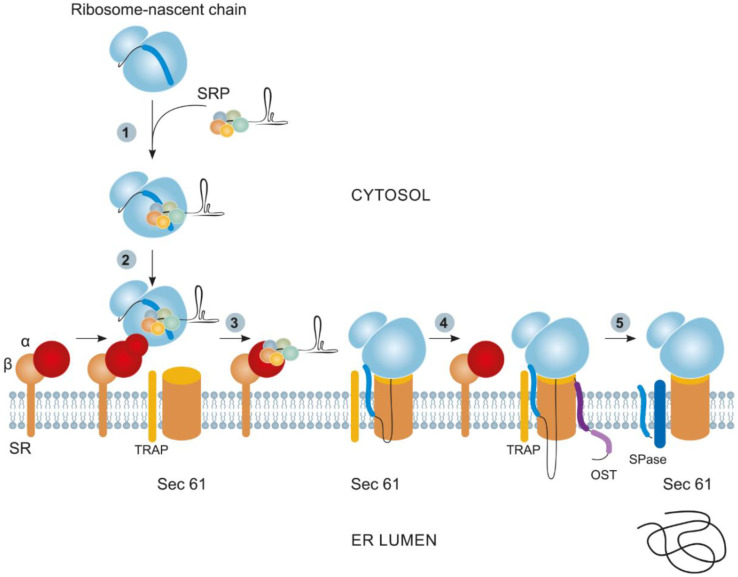
Figure 1.
The cotranslational protein targeting pathway: (1) The SRP binds a signal sequence (dark blue) as it emerges from a ribosome to form the RNC–SRP complex; (2) the RNC–SRP complex docks with the ER membrane by binding to a cognate SRP receptor (SR, consisting of α and β subunits); (3) subsequently, the RNC is transferred from SR–SRP to translocon Sec61, resulting in the intercalation of the signal sequence into the translocon pore and its opening; (4) the nascent chain is translocated through the pore, and the SRP disengages from the SR; (5) concomitantly with translocation, the signal peptidase (SPase) and oligosaccharyltransferase (OST) enzyme complexes are recruited to the translocon to cleave the SP and add N-linked glycans to the nascent chain, respectively. The termination of the protein synthesis releases the nascent chain from the ribosome; the translocation is completed; and the protein folds in the ER lumen (adapted from [38] with permission).