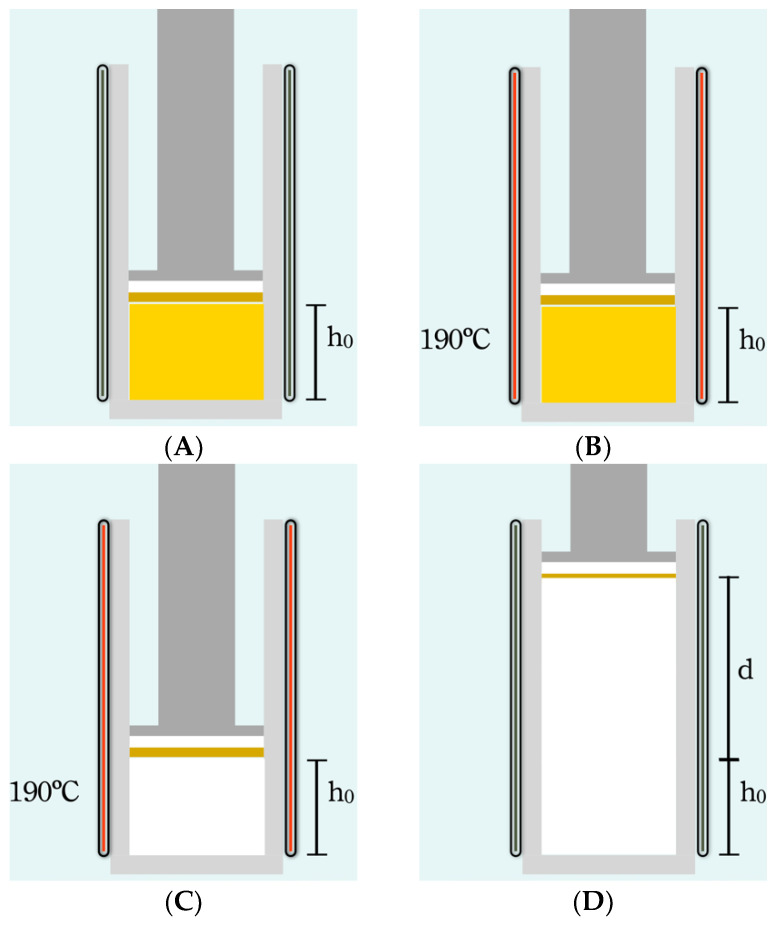
Figure 2.
Making the foam from the precursor. (A) The foam was made in the same mold; we use a tight piston that does not allow the gas to escape. We seal it with 5 Tn. (B) Heat it to 190 °C to decompose the AZO. The hydraulic press increases the load when the gas is released, up to 18 Tn for the lower-density foams 250 Kg/m3, up to 30 Tn for the higher-density foams 750 Kg/m3. For this reason, we could not make all the compositions for the higher-density foam, but only the 750 b (5.8% AZO) and 750 c (10.5% AZO). The other compositions break the seal. (C) When the pressure reaches the maximum, the entire AZO is decomposed; we turn off the heater and let the piston go up. (D) The increase in volume forms all the bubbles in the polymer. We cool the steel mold with water spray and squeeze the air for 5 min. Some of the foams broke when we removed the foam from the mold because there were still large amounts of gas in the core of the foam.