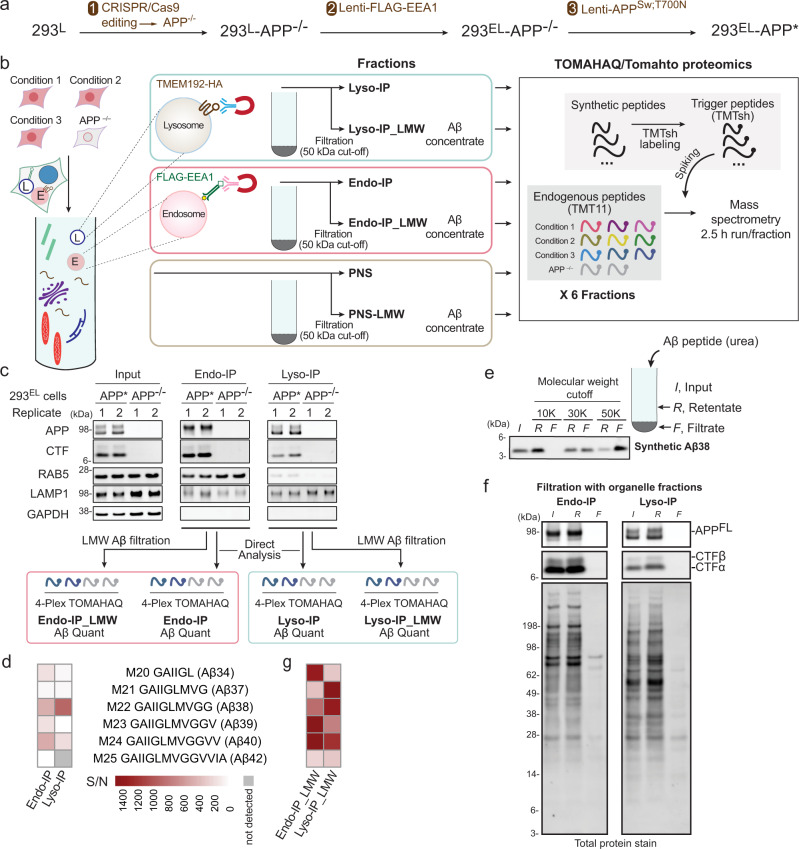
Fig. 5. Application of spatial endolysosomal proteomics to analysis of APP processing by γ-Secretase.
a APP in 293EL cells was deleted with CRISPR-Cas9 and APPSw;T700N expressed stably using a lentivirus to create 293EL-APP*. b The optimized workflow involves homogenization of cells to generate the post-nuclear supernatant (PNS) followed by Endo- or Lyso-IP, which are either used directly for TOMAHAQ proteomics via a multi-step workflow or solubilized in 8 M urea/0.5% NP-40 and LMW filtration using a 50 kDa filter to purify Aβ peptides for TOMAHAQ proteomics. c The indicated 293EL cells in biological duplicate (n = 2) were subjected to Endo- or Lyso-IP prior to immunoblotting (top panels) and analysis by TOMAHAQ with or without LMW filtration. d TOMAHAQ-TMT reporter ion signal-to-noise ratios for samples from panel c (without filtration). Background intensities in APP−/− cells were subtracted from those of test samples. e Analysis of synthetic Aβ38 passage through filters with distinct molecular weight cut-offs (representative of 3 experiments). Synthetic Aβ in 8 M urea (with 0.5% NP-40) was applied to the filter and centrifuged for 12 min at 14,000 × g. Input, filtrate, and retentate samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and peptides stained with Total Protein Stain. f Proteins released from either Endo- or Lyso-IPs with 8 M urea/0.5% NP-40 were subjected to filtration with a 50 kDa cut-off filter and the input, retentate and filtrate analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies or stain for total protein (representative of 3 experiments). g TOMAHAQ-TMT reporter ion signal-to-noise ratios for samples from panel c (with LMW filtration), as in panel d.